TechCrunch
TechCrunch
Google has near complete grip on the search market in Europe, with a regional market share in excess of 90%, according to Statcounter. Unsurprisingly, industry sources say a majority of travel bookings start as a Google search — giving the tech giant huge leverage over the coronavirus-hit sector.
More than half a dozen travel startups in Germany are united in a shared complaint that Google is abusing its search dominance in a number of ways they argue are negatively impacting their businesses.
Complaints we’ve heard from multiple sources in online travel range from Google forcing its own data standards on ad partners to Google unfairly extracting partner data to power its own competing products on the cheap.
Startups are limited in how much detail they can provide on the record about Google’s processes because the company requires advertising partners to sign NDAs to access its ad products. But this week German newspaper Handelsblatt reported on antitrust complaints from a number of local startups — including experience booking platform GetYourGuide and vacation rental search engine HomeToGo — which are accusing the tech giant of stealing content and data.
The group is considering filing a cartel complaint against Google, per its report.
We’ve also heard from multiple sources in the European travel sector that Google has exhibited a pattern of trying to secure the rights to travel partners’ content and data through contracts and service agreements.
One source, who did not wish to be identified for fear of retaliation against their business, told us: “Each travel partner has certain specialities in their business model but overall the strategy of Google has been the same: Grab as much data from your partners and build competing products with that data.”
Not OK, Google
This is now a very familiar complaint against Google. Crowdsourced reviews platform Yelp has been accusing the tech giant of stealing content for years. More recently, Genius got creative with a digital watermark that caught Google redhanded scraping lyrics content from its site which it pays to license (but Google does not). As Lily Allen might put it, it’s really not okay.
Last month’s congressional antitrust subcommittee hearing kicked off with exactly this accusation too — as chair David Cicilline barked at Google and Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai: “Why does Google steal content from honest businesses?” Pichai dodged the question by claiming he doesn’t agree with the characterization. But for Google and parent Alphabet there’s no dodging the antitrust drumbeat pounding violently in the company’s backyard.
In Europe, Google’s business already has a clutch of antitrust enforcements against it — starting three years ago, in a case which dated back six years at that point, with a record-breaking penalty for anti-competitive behavior in how it operated a product search service called Google Shopping. EU enforcements against Android and AdSense swiftly followed. Google is appealing all three decisions, even as it continues to expand its operations in lucrative verticals like travel.
The Commission’s 2017 finding that Google is dominant in the regional search market carried what lawmakers couch as a “special responsibility” to avoid breaching the bloc’s antitrust rules in any market in which Google plays. That finding puts the travel sector squarely in the frame, although not yet under formal probe by EU regulators (although they have opened an active probe of Google’s data collection practices, announced last year).
EU regulators are also examining a range of competition concerns over its proposed acquisition of Fitbit, delaying the merger while they consider whether the deal would further entrench Google’s position in the ad market by giving it access to a trove of Fitbit users’ health data that could be used for increased ad personalization.
But so far, on travel, the Commission has been keeping its powder dry.
Yet for around a decade the tech giant has been building out products that directly compete for travel bookings in growth areas like flight search. More recently it’s added hotels, vacation rentals and experiences — bringing its search tool into direct competition with an increasing range of third-party booking platforms which, at least in Europe, have no choice but to advertise on Google’s platform to drive customer acquisition.
One key acquisition underpinning Google’s travel ambitions dates back to 2010 — when it shelled out $700 million for ITA, a provider of flight information to airlines, travel agencies and online reservation systems. The same year it also picked up travel guide community, Ruba.
Google beat out a consortium of rivals for ITA, including Microsoft, Kayak, Expedia and Travelport, which relied on its data to power their own travel products — and had wanted to prevent Google getting its hands on the data.
Back then travel was already a huge segment of search and online commerce. And it’s continued to grow — worth close to $700 billion globally in 2018, per eMarketer (although the coronavirus crisis is likely to impact some recent growth projections, even as the public health crisis accelerates the industry’s transition to digital bookings) — all of which gives Google huge incentive to carve itself a bigger and bigger share of the pie.
This is what Google is aiming to do by building out ad units that cater to travelers’ searches by offering flights, vacation rentals and trip experiences, searchable without needing to leave Google’s platform.
Google defends this type of expansion by saying it’s just making life easier for the user by putting sought for information even closer to their search query. But competitors contend the choices it’s making are far more insidious. Simply put, they’re better for Google’s bottom line — and will ultimately result in less choice and innovation for consumers — is the core argument. The key contention is Google is only able to do this because it wields vast monopoly power in search, which gives it unfair access to travel rivals’ content and data.
It’s certainly notable that Alphabet hasn’t felt the need to shell out to acquire any of the major travel booking platforms since its ITA acquisition. Instead, its market might allow it to repackage and monetize rival travel platforms’ data via an expanding array of its own vertical travel search products.
One of the German consortia of travel startups with a major beef against Google is Berlin-based HomeToGo. The vacation rentals platform confirmed to TechCrunch it has filed an antitrust complaint against the company with the European Commission.
It told us it’s watched with alarm as Google introduced a new ad unit in search results which promotes a vacation rental search and booking experience — displaying property thumbnails, alongside locations and prices plotted on a map — right from inside Google’s platform.
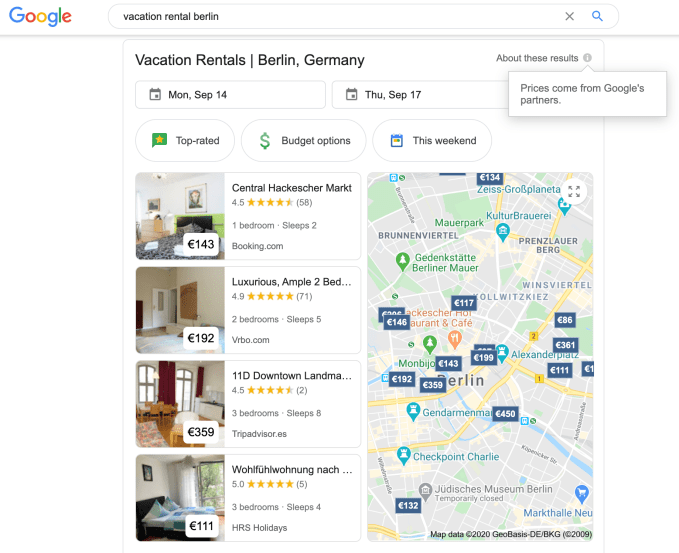


Screengrab showing Google vacation rental ad unit, populated with content from a range of partners
Discussing the complaint, HomeToGo CEO and co-founder, Dr Patrick Andrae, told us: “Due to the monopoly Google has in horizontal search, just by having this kind of access [to the vast majority of European Internet searchers], they’re so top of the funnel that they theoretically can go into any vertical. And with the power of their monopoly they can turn on products there without doing any prior investment in it.
“Anyone else has to work a lot on SEO strategies and these kind of things to slowly go up in the ranking but Google can just snap its fingers and say, basically, tomorrow I want to have a product.”
The complaint is not just that Google has built a competing ad product in vacation rentals but — following what has become a standard colonizing playbook for seemingly any vertical area Google sees is grabbing traffic — its packaging of the competing product is so fully featured and eye-catching that it results in greater prominence for Google’s ad versus organic search results (or indeed paid ad links) where rivals may appear as plain-old blue links.
“They create this giant, colorful super CTA [call-to-action], as we call it — this one-box thing — where everything is clickable and leads you into the Google product,” said Andrae. “They explain that it’s better for the user experience but no one ever said that the user wants to have a one-box there from Google. Or why shouldn’t it be a one-box from HomeToGo? Or why shouldn’t it be a one-box in the flight world from Kayak? Or in the hotel world from Trivago? So why is it just the Google product that’s colorful, nice, and showing up?”
Andrae argues that the design of the unit is intended to give the user the impression that “Google has everything there,” on its platform. So, y’know, why go looking elsewhere for a vertical search engine?
He also points out that the special unit is not available to competitors. “You cannot buy it,” he said. “So even if you would like to have this prominent kind of placement you cannot buy that as a third-party company. Even if you would like to pay money for it — I’m not talking about being in the product itself, that’s another topic — but just having the same kind of advertisement, because it is what they do — they advertise their own product there for free — and this is our complaint.”
Pay with your data
In 2017, when the Commission slapped Google with the first record-breaking penalty over its search comparison service — finding it had systematically given prominent placement to its own comparison shopping service over and above rival services in organic search results — competition chief Margrethe Vestager disclosed it had also received complaints about Google’s behavior in the travel sector.
Asked about the sector’s concerns now, some three years later, a Commission spokeswoman told us it’s “monitoring the markets concerned” — but declined to comment on any specific gripes.
Here’s another complaint: GetYourGuide, a Berlin-based travel startup that’s created a discovery and booking platform for travel tours and experiences, has similar concerns about Google’s designs on travel experience booking — another travel segment the tech giant is moving into via its own eye-catching ad units flogging experiences.
“They want to create experience products now directly on Google search itself, with the aim that ultimately people can book these type of things on Google,” said GetYourGuide CEO and co-founder Johannes Reck. “What Google tries to do now is they try to get [travel startups’] content and our data in order to create new competitive products on Google.”
The startup is unhappy, for example, that a “Things to do” ad product Google shows in its search results doesn’t link to GetYourGuide’s own search page — which would be the equivalent and competing third party product.
“Google will not allow us to link them into our search but only into the details page so the customer sees even less of our brand,” he said. “Or in Maps, for instance, if you go to Eiffel Tower and press to book tickets you don’t see any of GetYourGuide despite us fulfilling that order.”
He also rejects Google’s claim against this sort of complaint that it’s simply “doing the right thing for the user” by not linking them out to the rival platform. “We do know from our data that users convert better and spend more time on our site and have higher engagement rates when we link them into our search and then deeper down into the funnel,” he told TechCrunch. “What Google is saying is not that it serves the user — it serves Google and it serves their profits. Because the deeper down the funnel that you link, the user will either buy or they will bounce back to Google and search for the next product. If you link into searches — if you don’t verticalize as much — then the user will end up in a different ecosystem and might not bounce back to Google.”
“As a partner [of Google] you have limited choice to participate [in its ad products]. You do need to give Google that content and then Google will try to move as many of the customers to them,” Reck added. “I don’t think there ever will be a world where booking.com or Expedia or GetYourGuide will disappear — rather our brands will start to disappear.
“That is something that I think ultimately is bad for the customer and only serves Google, again, because the customer will, in the long run, have no other choice and no other visibility on how he can get to choice than to go through Google because our brands will basically be hidden behind a Google wall. That will turn Google firmly away from what their original mission was… to steer people to the most relevant content on the web… Now they are trying to be completely the opposite; they’re trying to be the Amazon or Alibaba of travel and try to keep and contain people in their ecosystem.”
During the congressional antitrust subcommittee hearing last month Pichai claimed Google faces fierce competition in travel. Again, Reck contends that’s simply not true. “In Europe more than 75% of travelers go to Google to search for travel and all those users are free,” he said. “Everyone else in the travel industry pays Google top dollar… for these queries. Which competition exactly is he referring to?”
“[Pichai] then claimed that they’re not leveraging partners’ content — that’s not accurate. If you look at Google if you want to be in the top results these days you either pay or you give them data so that they can build their own products into search.”
“This dates back 10 years now when they acquired ITA software, which is the leading data provider for flights,” Reck added. “They’ve just paved their way into travel. I think their intent is very clear at this point that they have no interest in their partners — or their customers for that matter, who like the choice that’s being offered on Google.
“What they want to morph into, basically, is to turn Google into the Amazon of travel where everyone else may be a content provider or a fulfillment agent but the consumer has no choice but to go through Google. I think that is the key intent here. They want to limit consumer choice. And they want to monopolise the space. We don’t want that and we will fight that. And if that means we need to go to the EU Commission to protect our and the customers’ interests then we’ll do that and we’re currently reviewing that option.”
The looming harm for consumers around reduced choice could manifest in poorer customer service, which is an area vertical players tend to focus on — whereas Google, as a platform funnel, does not.
Another German travel startup — Munich-based FlixBus — was also willing to go on the record with concerns about the impact of Google’s market power on the sector, despite not being in the same position as its business is not an aggregator.
Nonetheless, FlixBus founder and CEO Jochen Engert called on regional lawmakers to act against what he described as Google’s “systematic abuses” of market dominance.
“We call on the politicians in Germany and the EU to now work for fair competition on the internet. It must be forbidden that monopolistic companies like Google abuse their market power, especially in times of crisis, and prevent competition for the benefit of the customer due to their dominance,” he told us. “Google systematically abuses its dominant market position to seal off access to customers from competitors and gets away with it time and again. It is only a matter of time before other industries and business models, in addition to travel, hotel and flight bookings, are permanently threatened.
“For FlixMobility [FlixBus’ parent company] as an internationally positioned market leader with its own platform, technology and our unique content, the situation is more relaxed than for smaller startups or those which also aggregate content such as Google. Nevertheless, in our opinion Google should be obliged to list and market its own products in search results on an equal footing with comparable offers. Here regulation must not stand by and watch for too long, but must react before Google irretrievably controls customer access and excludes competition.”
GetYourGuide’s Reck expressed hope that German lawmakers might be able to offer more expeditious relief to the sector than the European Commission — whose competition investigations typically grind through the details for years.
“The German government is actually very alert at this point in time,” he said. “They’re currently working on a new competition legislation that they will put in place probably within the next six months. It’s already in the making — and that will also be addressed to exactly that type of behavior of global, quasi-monopolistic platforms crossing the demarcation line, moving into other fields and trying to leverage their monopoly in order to create synergies in adjacent fields and crowd out competition.”
Asked what kind of intervention he would like to see regulators make against Google, Reck suggests its business should be regulated akin to a utility — advocating for controls on data, including around the openness of data, to level the playing field.
Though he also told us he would be supportive of more radical measures, such as breaking Google up. (But, again, he says speed of intervention is of the essence.)
“If you look at all of the data that Google collects, whether that’s consumer reviews, availability from its partners, all of the content from its partners, all of the information that they have through Android, whether that’s geo-specific data, whether that is interests, whether that is contextual information, Google is training their algorithms day and night on this data, no one else can. But we all have to provide data to Google,” he said.
“That’s not a level playing field. We need to think about how we can have a more open data architecture, that obviously is compliant with our data privacy laws but where developers from anywhere can build products based on the Google platform… As a developer in travel it’s currently very hard for me to access any data from Google so I can build better products for consumers. And I think that really needs to change — Google needs to open us for us to create a more vibrant and competitive ecosystem.”
“At a national or EU level we need to have an updated legal code that allows for quick interventions,” Reck added, saying competition enforcement simply can’t carry on at the same pace as for the markets of the past. “Things are moving way too quickly for that. You need to take a completely new approach.
“As Google correctly pointed out consumer prices have fallen but falling consumer prices is the weapon in tech; offering products for free allows you to gain market share in order to crowd out competition, which again leaves less choice for the customer, so I think we need to think about how we think about tech and platforms in new ways.”
The Commission is currently consulting on whether competition regulators need a new tool to be able to intervene more quickly in digital markets. But there’s more than a trace of irony that its adherence to process means further delay as regulators question whether they need more power to intervene in digital markets to prevent tipping, instead of acting on longstanding complaints of market abuse attached to the 800-lb gorilla of internet search — with its “special responsibility” not to trample on other markets.
Reached for comment on the travel startups’ complaints, a Google spokeswoman sent us this statement:
There are now more ways than ever to find information online, and for travel searches, people can easily choose from an array of specialized sites, like TripAdvisor, Kayak, Expedia and many more. With Google Search, we aim to provide the most helpful and relevant results possible to create the best experience for users around the world and deliver valuable traffic to travel companies.
During the pandemic, we’ve been working hard with our partners in the travel industry to help them protect their businesses and look toward recovery. We launched new tools for airlines so they can better predict consumer demand and plan their routes. For hotels, we expanded our ‘pay per stay’ program globally to shift the risk of cancellation from our partners to us. And we’ve updated our search products so consumers can make informed decisions when planning future travel, further reducing the risk of cancellation.
The company did not respond to our request for a response to claims we heard that it seeks to secure rights to partners’ content and data via contracts and service agreements.
No relief
In another sign of the growing rift between Google and its travel partners in Europe, German startups in the sector banded together to press it for better terms during the coronavirus crisis earlier this year — accusing the tech giant of being inflexible over payments for ads they’d run before the crisis hit. This meant they were left with a huge hole in their balance sheets after making mass refunds for travelers who could no longer take their planned trip. But the gorilla wasn’t sympathetic, demanding full payment immediately.
Asked what happened after TechCrunch reported on their concerns at the end of April, Reck said Google went silent for a few weeks. But as soon as the travel market started picking up in Germany — and GetYourGuide decided it needed to start advertising on Google again — it reissued the demand for full payment.
GetYourGuide says it was left with no choice but to pay, given it needed to be able to run Google ads.
Reck describes the recovery package Google offered after it made the payment as “a Google recovery package” — as it was tied to GetYourGuide spending a large amount on YouTube ads in order to get a small discount.
The offer would recoup only a “fraction” of GetYourGuide’s original losses on Google ads during the peak of the COVID-19 crisis, per Reck. “YouTube obviously is not where we lost the money. We lost the money in search where we had high-intent customers, Google customers that wanted to come and shop. So that to us was [another] slap in the face,” he added.
]]>
TechCrunch
TechCrunch
Google has near complete grip on the search market in Europe, with a regional market share in excess of 90%, according to Statcounter. Unsurprisingly, industry sources say a majority of travel bookings start as a Google search — giving the tech giant huge leverage over the coronavirus-hit sector.
More than half a dozen travel startups in Germany are united in a shared complaint that Google is abusing its search dominance in a number of ways they argue are negatively impacting their businesses.
Complaints we’ve heard from multiple sources in online travel range from Google forcing its own data standards on ad partners to Google unfairly extracting partner data to power its own competing products on the cheap.
Startups are limited in how much detail they can provide on the record about Google’s processes because the company requires advertising partners to sign NDAs to access its ad products. But this week German newspaper Handelsblatt reported on antitrust complaints from a number of local startups — including experience booking platform GetYourGuide and vacation rental search engine HomeToGo — which are accusing the tech giant of stealing content and data.
The group is considering filing a cartel complaint against Google, per its report.
We’ve also heard from multiple sources in the European travel sector that Google has exhibited a pattern of trying to secure the rights to travel partners’ content and data through contracts and service agreements.
One source, who did not wish to be identified for fear of retaliation against their business, told us: “Each travel partner has certain specialities in their business model but overall the strategy of Google has been the same: Grab as much data from your partners and build competing products with that data.”
Not OK, Google
This is now a very familiar complaint against Google. Crowdsourced reviews platform Yelp has been accusing the tech giant of stealing content for years. More recently, Genius got creative with a digital watermark that caught Google redhanded scraping lyrics content from its site which it pays to license (but Google does not). As Lily Allen might put it, it’s really not okay.
Last month’s congressional antitrust subcommittee hearing kicked off with exactly this accusation too — as chair David Cicilline barked at Google and Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai: “Why does Google steal content from honest businesses?” Pichai dodged the question by claiming he doesn’t agree with the characterization. But for Google and parent Alphabet there’s no dodging the antitrust drumbeat pounding violently in the company’s backyard.
In Europe, Google’s business already has a clutch of antitrust enforcements against it — starting three years ago, in a case which dated back six years at that point, with a record-breaking penalty for anti-competitive behavior in how it operated a product search service called Google Shopping. EU enforcements against Android and AdSense swiftly followed. Google is appealing all three decisions, even as it continues to expand its operations in lucrative verticals like travel.
The Commission’s 2017 finding that Google is dominant in the regional search market carried what lawmakers couch as a “special responsibility” to avoid breaching the bloc’s antitrust rules in any market in which Google plays. That finding puts the travel sector squarely in the frame, although not yet under formal probe by EU regulators (although they have opened an active probe of Google’s data collection practices, announced last year).
EU regulators are also examining a range of competition concerns over its proposed acquisition of Fitbit, delaying the merger while they consider whether the deal would further entrench Google’s position in the ad market by giving it access to a trove of Fitbit users’ health data that could be used for increased ad personalization.
But so far, on travel, the Commission has been keeping its powder dry.
Yet for around a decade the tech giant has been building out products that directly compete for travel bookings in growth areas like flight search. More recently it’s added hotels, vacation rentals and experiences — bringing its search tool into direct competition with an increasing range of third-party booking platforms which, at least in Europe, have no choice but to advertise on Google’s platform to drive customer acquisition.
One key acquisition underpinning Google’s travel ambitions dates back to 2010 — when it shelled out $700 million for ITA, a provider of flight information to airlines, travel agencies and online reservation systems. The same year it also picked up travel guide community, Ruba.
Google beat out a consortium of rivals for ITA, including Microsoft, Kayak, Expedia and Travelport, which relied on its data to power their own travel products — and had wanted to prevent Google getting its hands on the data.
Back then travel was already a huge segment of search and online commerce. And it’s continued to grow — worth close to $700 billion globally in 2018, per eMarketer (although the coronavirus crisis is likely to impact some recent growth projections, even as the public health crisis accelerates the industry’s transition to digital bookings) — all of which gives Google huge incentive to carve itself a bigger and bigger share of the pie.
This is what Google is aiming to do by building out ad units that cater to travelers’ searches by offering flights, vacation rentals and trip experiences, searchable without needing to leave Google’s platform.
Google defends this type of expansion by saying it’s just making life easier for the user by putting sought for information even closer to their search query. But competitors contend the choices it’s making are far more insidious. Simply put, they’re better for Google’s bottom line — and will ultimately result in less choice and innovation for consumers — is the core argument. The key contention is Google is only able to do this because it wields vast monopoly power in search, which gives it unfair access to travel rivals’ content and data.
It’s certainly notable that Alphabet hasn’t felt the need to shell out to acquire any of the major travel booking platforms since its ITA acquisition. Instead, its market might allow it to repackage and monetize rival travel platforms’ data via an expanding array of its own vertical travel search products.
One of the German consortia of travel startups with a major beef against Google is Berlin-based HomeToGo. The vacation rentals platform confirmed to TechCrunch it has filed an antitrust complaint against the company with the European Commission.
It told us it’s watched with alarm as Google introduced a new ad unit in search results which promotes a vacation rental search and booking experience — displaying property thumbnails, alongside locations and prices plotted on a map — right from inside Google’s platform.



Screengrab showing Google vacation rental ad unit, populated with content from a range of partners
Discussing the complaint, HomeToGo CEO and co-founder, Dr Patrick Andrae, told us: “Due to the monopoly Google has in horizontal search, just by having this kind of access [to the vast majority of European Internet searchers], they’re so top of the funnel that they theoretically can go into any vertical. And with the power of their monopoly they can turn on products there without doing any prior investment in it.
“Anyone else has to work a lot on SEO strategies and these kind of things to slowly go up in the ranking but Google can just snap its fingers and say, basically, tomorrow I want to have a product.”
The complaint is not just that Google has built a competing ad product in vacation rentals but — following what has become a standard colonizing playbook for seemingly any vertical area Google sees is grabbing traffic — its packaging of the competing product is so fully featured and eye-catching that it results in greater prominence for Google’s ad versus organic search results (or indeed paid ad links) where rivals may appear as plain-old blue links.
“They create this giant, colorful super CTA [call-to-action], as we call it — this one-box thing — where everything is clickable and leads you into the Google product,” said Andrae. “They explain that it’s better for the user experience but no one ever said that the user wants to have a one-box there from Google. Or why shouldn’t it be a one-box from HomeToGo? Or why shouldn’t it be a one-box in the flight world from Kayak? Or in the hotel world from Trivago? So why is it just the Google product that’s colorful, nice, and showing up?”
Andrae argues that the design of the unit is intended to give the user the impression that “Google has everything there,” on its platform. So, y’know, why go looking elsewhere for a vertical search engine?
He also points out that the special unit is not available to competitors. “You cannot buy it,” he said. “So even if you would like to have this prominent kind of placement you cannot buy that as a third-party company. Even if you would like to pay money for it — I’m not talking about being in the product itself, that’s another topic — but just having the same kind of advertisement, because it is what they do — they advertise their own product there for free — and this is our complaint.”
Pay with your data
In 2017, when the Commission slapped Google with the first record-breaking penalty over its search comparison service — finding it had systematically given prominent placement to its own comparison shopping service over and above rival services in organic search results — competition chief Margrethe Vestager disclosed it had also received complaints about Google’s behavior in the travel sector.
Asked about the sector’s concerns now, some three years later, a Commission spokeswoman told us it’s “monitoring the markets concerned” — but declined to comment on any specific gripes.
Here’s another complaint: GetYourGuide, a Berlin-based travel startup that’s created a discovery and booking platform for travel tours and experiences, has similar concerns about Google’s designs on travel experience booking — another travel segment the tech giant is moving into via its own eye-catching ad units flogging experiences.
“They want to create experience products now directly on Google search itself, with the aim that ultimately people can book these type of things on Google,” said GetYourGuide CEO and co-founder Johannes Reck. “What Google tries to do now is they try to get [travel startups’] content and our data in order to create new competitive products on Google.”
The startup is unhappy, for example, that a “Things to do” ad product Google shows in its search results doesn’t link to GetYourGuide’s own search page — which would be the equivalent and competing third party product.
“Google will not allow us to link them into our search but only into the details page so the customer sees even less of our brand,” he said. “Or in Maps, for instance, if you go to Eiffel Tower and press to book tickets you don’t see any of GetYourGuide despite us fulfilling that order.”
He also rejects Google’s claim against this sort of complaint that it’s simply “doing the right thing for the user” by not linking them out to the rival platform. “We do know from our data that users convert better and spend more time on our site and have higher engagement rates when we link them into our search and then deeper down into the funnel,” he told TechCrunch. “What Google is saying is not that it serves the user — it serves Google and it serves their profits. Because the deeper down the funnel that you link, the user will either buy or they will bounce back to Google and search for the next product. If you link into searches — if you don’t verticalize as much — then the user will end up in a different ecosystem and might not bounce back to Google.”
“As a partner [of Google] you have limited choice to participate [in its ad products]. You do need to give Google that content and then Google will try to move as many of the customers to them,” Reck added. “I don’t think there ever will be a world where booking.com or Expedia or GetYourGuide will disappear — rather our brands will start to disappear.
“That is something that I think ultimately is bad for the customer and only serves Google, again, because the customer will, in the long run, have no other choice and no other visibility on how he can get to choice than to go through Google because our brands will basically be hidden behind a Google wall. That will turn Google firmly away from what their original mission was… to steer people to the most relevant content on the web… Now they are trying to be completely the opposite; they’re trying to be the Amazon or Alibaba of travel and try to keep and contain people in their ecosystem.”
During the congressional antitrust subcommittee hearing last month Pichai claimed Google faces fierce competition in travel. Again, Reck contends that’s simply not true. “In Europe more than 75% of travelers go to Google to search for travel and all those users are free,” he said. “Everyone else in the travel industry pays Google top dollar… for these queries. Which competition exactly is he referring to?”
“[Pichai] then claimed that they’re not leveraging partners’ content — that’s not accurate. If you look at Google if you want to be in the top results these days you either pay or you give them data so that they can build their own products into search.”
“This dates back 10 years now when they acquired ITA software, which is the leading data provider for flights,” Reck added. “They’ve just paved their way into travel. I think their intent is very clear at this point that they have no interest in their partners — or their customers for that matter, who like the choice that’s being offered on Google.
“What they want to morph into, basically, is to turn Google into the Amazon of travel where everyone else may be a content provider or a fulfillment agent but the consumer has no choice but to go through Google. I think that is the key intent here. They want to limit consumer choice. And they want to monopolise the space. We don’t want that and we will fight that. And if that means we need to go to the EU Commission to protect our and the customers’ interests then we’ll do that and we’re currently reviewing that option.”
The looming harm for consumers around reduced choice could manifest in poorer customer service, which is an area vertical players tend to focus on — whereas Google, as a platform funnel, does not.
Another German travel startup — Munich-based FlixBus — was also willing to go on the record with concerns about the impact of Google’s market power on the sector, despite not being in the same position as its business is not an aggregator.
Nonetheless, FlixBus founder and CEO Jochen Engert called on regional lawmakers to act against what he described as Google’s “systematic abuses” of market dominance.
“We call on the politicians in Germany and the EU to now work for fair competition on the internet. It must be forbidden that monopolistic companies like Google abuse their market power, especially in times of crisis, and prevent competition for the benefit of the customer due to their dominance,” he told us. “Google systematically abuses its dominant market position to seal off access to customers from competitors and gets away with it time and again. It is only a matter of time before other industries and business models, in addition to travel, hotel and flight bookings, are permanently threatened.
“For FlixMobility [FlixBus’ parent company] as an internationally positioned market leader with its own platform, technology and our unique content, the situation is more relaxed than for smaller startups or those which also aggregate content such as Google. Nevertheless, in our opinion Google should be obliged to list and market its own products in search results on an equal footing with comparable offers. Here regulation must not stand by and watch for too long, but must react before Google irretrievably controls customer access and excludes competition.”
GetYourGuide’s Reck expressed hope that German lawmakers might be able to offer more expeditious relief to the sector than the European Commission — whose competition investigations typically grind through the details for years.
“The German government is actually very alert at this point in time,” he said. “They’re currently working on a new competition legislation that they will put in place probably within the next six months. It’s already in the making — and that will also be addressed to exactly that type of behavior of global, quasi-monopolistic platforms crossing the demarcation line, moving into other fields and trying to leverage their monopoly in order to create synergies in adjacent fields and crowd out competition.”
Asked what kind of intervention he would like to see regulators make against Google, Reck suggests its business should be regulated akin to a utility — advocating for controls on data, including around the openness of data, to level the playing field.
Though he also told us he would be supportive of more radical measures, such as breaking Google up. (But, again, he says speed of intervention is of the essence.)
“If you look at all of the data that Google collects, whether that’s consumer reviews, availability from its partners, all of the content from its partners, all of the information that they have through Android, whether that’s geo-specific data, whether that is interests, whether that is contextual information, Google is training their algorithms day and night on this data, no one else can. But we all have to provide data to Google,” he said.
“That’s not a level playing field. We need to think about how we can have a more open data architecture, that obviously is compliant with our data privacy laws but where developers from anywhere can build products based on the Google platform… As a developer in travel it’s currently very hard for me to access any data from Google so I can build better products for consumers. And I think that really needs to change — Google needs to open us for us to create a more vibrant and competitive ecosystem.”
“At a national or EU level we need to have an updated legal code that allows for quick interventions,” Reck added, saying competition enforcement simply can’t carry on at the same pace as for the markets of the past. “Things are moving way too quickly for that. You need to take a completely new approach.
“As Google correctly pointed out consumer prices have fallen but falling consumer prices is the weapon in tech; offering products for free allows you to gain market share in order to crowd out competition, which again leaves less choice for the customer, so I think we need to think about how we think about tech and platforms in new ways.”
The Commission is currently consulting on whether competition regulators need a new tool to be able to intervene more quickly in digital markets. But there’s more than a trace of irony that its adherence to process means further delay as regulators question whether they need more power to intervene in digital markets to prevent tipping, instead of acting on longstanding complaints of market abuse attached to the 800-lb gorilla of internet search — with its “special responsibility” not to trample on other markets.
Reached for comment on the travel startups’ complaints, a Google spokeswoman sent us this statement:
There are now more ways than ever to find information online, and for travel searches, people can easily choose from an array of specialized sites, like TripAdvisor, Kayak, Expedia and many more. With Google Search, we aim to provide the most helpful and relevant results possible to create the best experience for users around the world and deliver valuable traffic to travel companies.
During the pandemic, we’ve been working hard with our partners in the travel industry to help them protect their businesses and look toward recovery. We launched new tools for airlines so they can better predict consumer demand and plan their routes. For hotels, we expanded our ‘pay per stay’ program globally to shift the risk of cancellation from our partners to us. And we’ve updated our search products so consumers can make informed decisions when planning future travel, further reducing the risk of cancellation.
The company did not respond to our request for a response to claims we heard that it seeks to secure rights to partners’ content and data via contracts and service agreements.
No relief
In another sign of the growing rift between Google and its travel partners in Europe, German startups in the sector banded together to press it for better terms during the coronavirus crisis earlier this year — accusing the tech giant of being inflexible over payments for ads they’d run before the crisis hit. This meant they were left with a huge hole in their balance sheets after making mass refunds for travelers who could no longer take their planned trip. But the gorilla wasn’t sympathetic, demanding full payment immediately.
Asked what happened after TechCrunch reported on their concerns at the end of April, Reck said Google went silent for a few weeks. But as soon as the travel market started picking up in Germany — and GetYourGuide decided it needed to start advertising on Google again — it reissued the demand for full payment.
GetYourGuide says it was left with no choice but to pay, given it needed to be able to run Google ads.
Reck describes the recovery package Google offered after it made the payment as “a Google recovery package” — as it was tied to GetYourGuide spending a large amount on YouTube ads in order to get a small discount.
The offer would recoup only a “fraction” of GetYourGuide’s original losses on Google ads during the peak of the COVID-19 crisis, per Reck. “YouTube obviously is not where we lost the money. We lost the money in search where we had high-intent customers, Google customers that wanted to come and shop. So that to us was [another] slap in the face,” he added.
]]>
TechCrunch
TechCrunch
The suits will argue that mass surveillance of Internet users to carry out real-time bidding ad auctions cannot possibly be compatible with strict EU laws around consent to process personal data.
The litigants believe the collective claims could exceed €10BN, should they eventually prevail in their arguments — though such legal actions can take several years to work their way through the courts.
In the UK, the case may also face some legal hurdles given the lack of an established model for pursuing collective damages in cases relating to data rights. Though there are signs that’s changing.
Non-profit foundation, The Privacy Collective, has filed one case today with the District Court of Amsterdam, accusing the two data broker giants of breaching the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in their processing and sharing of people’s information via third party tracking cookies and other adtech methods.
The Dutch case, which is being led by law-firm bureau Brandeis, is the biggest-ever class action in The Netherlands related to violation of the GDPR — with the claimant foundation representing the interests of all Dutch citizens whose personal data has been used without their consent and knowledge by Oracle and Salesforce.
A similar case is due to be filed later this month at the High Court in London England, which will make reference to the GDPR and the UK’s PECR (Privacy of Electronic Communications Regulation) — the latter governing the use of personal data for marketing communications. The case there is being led by law firm Cadwalader.
Under GDPR, consent for processing EU citizens’ personal data must be informed, specific and freely given. The regulation also confers rights on individuals around their data — such as the ability to receive a copy of their personal information.
It’s those requirements the litigation is focused on, with the cases set to argue that the tech giants’ third party tracking cookies, BlueKai and Krux — trackers that are hosted on scores of popular websites, such as Amazon, Booking.com, Dropbox, Reddit and Spotify to name a few — along with a number of other tracking techniques are being used to misuse Europeans’ data on a massive scale.
Per Oracle marketing materials, its Data Cloud and BlueKai Marketplace provider partners with access to some 2BN global consumer profiles. (Meanwhile, as we reported in June, BlueKai suffered a data breach that exposed billions of those records to the open web.)
While Salesforce claims its marketing cloud ‘interacts’ with more than 3BN browsers and devices monthly.
Both companies have grown their tracking and targeting capabilities via acquisition for years; Oracle bagging BlueKai in 2014 — and Salesforce snaffling Krux in 2016.
Discussing the lawsuit in a telephone call with TechCrunch, Dr Rebecca Rumbul, class representative and claimant in England & Wales, said: “There is, I think, no way that any normal person can really give informed consent to the way in which their data is going to be processed by the cookies that have been placed by Oracle and Salesforce.
“When you start digging into it there are numerous, fairly pernicious ways in which these cookies can and probably do operate — such as cookie syncing, and the aggregation of personal data — so there’s really, really serious privacy concerns there.”
The real-time-bidding (RTB) process that the pair’s tracking cookies and techniques feed, enabling the background, high velocity trading of profiles of individual web users as they browse in order to run dynamic ad auctions and serve behavioral ads targeting their interests, has, in recent years, been subject to a number of GDPR complaints, including in the UK.
These complaints argue that RTB’s handling of people’s information is a breach of the regulation because it’s inherently insecure to broadcast data to so many other entities — while, conversely, GDPR bakes in a requirement for privacy by design and default.
The UK Information Commissioner’s Office has, meanwhile, accepted for well over a year that adtech has a lawfulness problem. But the regulator has so far sat on its hands, instead of enforcing the law — leaving the complainants dangling. (Last year, Ireland’s DPC opened a formal investigation of Google’s adtech, following a similar complaint, but has yet to issue a single GDPR decision in a cross-border complaint — leading to concerns of an enforcement bottleneck.)
The two lawsuits targeting RTB aren’t focused on the security allegation, per Rumbul, but are mostly concerned with consent and data access rights.
She confirms they opted to litigate rather than trying to try a regulatory complaint route as a way of exercising their rights given the “David vs Goliath” nature of bringing claims against the tech giants in question.
“If I was just one tiny person trying to complaint to Oracle and trying to use the UK Information Commissioner to achieve that… they simply do not have the resources to direct at one complaint from one person against a company like Oracle — in terms of this kind of scale,” Rumbul told TechCrunch.
“In terms of being able to demonstrate harm, that’s quite a lot of work and what you get back in recompense would probably be quite small. It certainly wouldn’t compensate me for the time I would spend on it… Whereas doing it as a representative class action I can represent everyone in the UK that has been affected by this.
“The sums of money then work — in terms of the depths of Oracle’s pockets, the costs of litigation, which are enormous, and the fact that, hopefully, doing it this way, in a very large-scale, very public forum it’s not just about getting money back at the end of it; it’s about trying to achieve more standardized change in the industry.”
“If Salesforce and Oracle are not successful in fighting this then hopefully that send out ripples across the adtech industry as a whole — encouraging those that are using these quite pernicious cookies to change their behaviours,” she added.
The litigation is being funded by Innsworth, a litigation funder which is also funding Walter Merricks’ class action for 46 million consumers against Mastercard in London courts. And the GDPR appears to be helping to change the class action landscape in the UK — as it allows individuals to take private legal action. The framework can also support third parties to bring claims for redress on behalf of individuals. While changes to domestic consumer rights law also appear to be driving class actions.
Commenting in a statement, Ian Garrard, managing director of Innsworth Advisors, said: “The development of class action regimes in the UK and the availability of collective redress in the EU/EEA mean Innsworth can put money to work enabling access to justice for millions of individuals whose personal data has been misused.”
A separate and still ongoing lawsuit in the UK, which is seeking damages from Google on behalf of Safari users whose privacy settings it historically ignored, also looks to have bolstered the prospects of class action style legal actions related to data issues.
While the courts initially tossed the suit last year, the appeals court overturned that ruling — rejecting Google’s argument that UK and EU law requires “proof of causation and consequential damage” in order to bring a claim related to loss of control of data.
The judge said the claimant did not need to prove “pecuniary loss or distress” to recover damages, and also allowed the class to proceed without all the members having the same interest.
Discussing that case, Rumbul suggests a pending final judgement there (likely next year) may have a bearing on whether the lawsuit she’s involved with can be taken forward in the UK.
“I’m very much hoping that the UK judiciary are open to seeing these kind of cases come forward because without these kinds of things as very large class actions it’s almost like closing the door on this whole sphere of litigation. If there’s a legal ruling that says that case can’t go forward and therefore this case can’t go forward I’d be fascinated to understand how the judiciary think we’d have any recourse to these private companies for these kind of actions,” she said.
Asked why the litigation has focused on Oracle and Saleforce, given there are so many firms involved in the adtech pipeline, she said: “I am not saying that they are necessarily the worst or the only companies that are doing this. They are however huge, huge international multimillion-billion dollar companies. And they specifically went out and purchased different bits of adtech software, like BlueKai, in order to bolster their presence in this area — to bolster their own profits.
“This was a strategic business decision that they made to move into this space and become massive players. So in terms of the adtech marketplace they are very, very big players. If they are able to be held to account for this then it will hopefully change the industry as a whole. It will hopefully reduce the places to hide for the other more pernicious cookie manufacturers out there. And obviously they have huge, huge revenues so in terms of targeting people who are doing a lot of harm and that can afford to compensate people these are the right companies to be targeting.”
Rumbul also told us The Privacy Collective is looking to collect stories from web users who feel they have experienced harm related to online tracking.
“There’s plenty of evidence out there to show that how these cookies work means you can have very, very egregious outcomes for people at an individual level,” she added. “Whether that can be related to personal finance, to manipulation of addictive behaviors, whatever, these are all very, very possible — and they cover every aspect of our lives.”
Consumers in England and Wales and the Netherlands are being encouraged to register their support of the actions via The Privacy Collective’s website.
In a statement, Christiaan Alberdingk Thijm, lead lawyer at Brandeis, said: “Your data is being sold off in real-time to the highest bidder, in a flagrant violation of EU data protection regulations. This ad-targeting technology is insidious in that most people are unaware of its impact or the violations of privacy and data rights it entails. Within this adtech environment, Oracle and Salesforce perform activities which violate European privacy rules on a daily basis, but this is the first time they are being held to account. These cases will draw attention to astronomical profits being made from people’s personal information, and the risks to individuals and society of this lack of accountability.”
“Thousands of organisations are processing billions of bid requests each week with at best inconsistent application of adequate technical and organisational measures to secure the data, and with little or no consideration as to the requirements of data protection law about international transfers of personal data. The GDPR gives us the tool to assert individuals’ rights. The class action means we can aggregate the harm done,” added partner Melis Acuner from Cadwalader in another supporting statement.
We reached out to Oracle and Salesforce for comment on the litigation.
Oracle EVP and general counsel, Dorian Daley, said:
The Privacy Collective knowingly filed a meritless action based on deliberate misrepresentations of the facts. As Oracle previously informed the Privacy Collective, Oracle has no direct role in the real-time bidding process (RTB), has a minimal data footprint in the EU, and has a comprehensive GDPR compliance program. Despite Oracle’s fulsome explanation, the Privacy Collective has decided to pursue its shake-down through litigation filed in bad faith. Oracle will vigorously defend against these baseless claims.
A spokeswoman for Salesforce sent us this statement:
At Salesforce, Trust is our #1 value and nothing is more important to us than the privacy and security of our corporate customers’ data. We design and build our services with privacy at the forefront, providing our corporate customers with tools to help them comply with their own obligations under applicable privacy laws — including the EU GDPR — to preserve the privacy rights of their own customers.
Salesforce and another Data Management Platform provider, have received a privacy related complaint from a Dutch group called The Privacy Collective. The claim applies to the Salesforce Audience Studio service and does not relate to any other Salesforce service.
Salesforce disagrees with the allegations and intends to demonstrate they are without merit.
Our comprehensive privacy program provides tools to help our customers preserve the privacy rights of their own customers. To read more about the tools we provide our corporate customers and our commitment to privacy, visit salesforce.com/privacy/products/
]]>
TechCrunch
TechCrunch
Over the years, the Bay Area-founded event has dealt with an internal clash as the gathering has grown larger and attracted a heavy presence from Silicon Valley’s wealthy tech class, with tales of turnkey experiences, air-conditioned camps, helicopters and lobster dinners. Now, under the shadow of a historic pandemic, the organization behind the massive, iconic event is desperately working to stick to its roots while avoiding financial ruin as it pivots the 2020 festival to a digital format with the pro bono help of some of its tech industry attendees.
With just a few weeks before the event is set to kick off, the organization is bringing together a group of technologists with backgrounds in virtual reality, blockchain, hypnotism and immersive theatre to create a web of hacked-together social products that they hope will capture the atmosphere of Burning Man.
Going virtual is an unprecedented move for an event that’s mere existence already seems to defy precedent.
Burning Man is held in late August every year inside Nevada’s Black Rock Desert. For nine days, the attendees, who refer to themselves as Burners, fill up the desolate landscape with massive art installations, stages and camps. Attendance has been climbing over the past several decades, to the point that the federal government got involved, creating a more than 170-page report arguing why the event’s attendance should be capped. More than 78,000 people attended in 2019.
It’s an escape from society in a shared social experience that doesn’t seem to be replicable elsewhere.
The Multiverse
Steven Blumenfeld became the CTO of Burning Man days before the org’s leaders publicly announced that, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the physical event was being abruptly canceled and the team was going all-in on a virtual gathering. Though the serial CTO expected the position to largely involve crusty tasks maintaining the event’s media infrastructure, he soon was pressed to rethink the front-end of a sprawling event that’s decades old and steeped in lore.
“My first inclination is, ‘Great! Let’s go build a big 3D VR world blah blah blah… So then I spent the first two weeks looking at what I had for staff, what I had for time frame, and what we could actually do,” Blumenfeld says. “There was just no way. And you know, I actually still wanted to do it. I wanted a challenge… but the reality was it just wasn’t going to happen.”
Burning Man is a massive undertaking, with a particularly deep emotional hold inside San Francisco, where it was first held in 1986, and by extension Silicon Valley. It isn’t all that surprising that when the Burning Man Project announced the event was making the move to a digital format, there was a rapid influx of community input to help decipher what an on-the-grid virtual Burning Man might look like.
“We had 14,000 people tell us they wanted to contribute in some way to a virtual Black Rock City,” said Kim Cook, the org’s director of art and civic engagement. “Some of them said what they wanted to contribute was love; so that’s cool. We also had around a thousand of them say they wanted to do developer-type work.”
Some of the groups that reached out to the Burning Man Project were companies that were willing to build a Burning Man experience but wanted official branding present. Despite a precarious financial position, Burning Man’s organizers declined help from these sponsors, citing the org’s adherence to “de-commodification” — a desire to prevent corporate infiltration of the event, eschewing advertising, branded stages and corporate partnerships.
Turning away from the professional studios, Blumenfeld and others settled on a network of small indie teams filled with Burners that were willing to develop the official digital experiences for the event on their own time.
A new moment for social networking
Eight projects eventually emerged as official “recognized universes,” each taking drastically different approaches to what a virtual Burning Man should look like. While some focus their efforts on virtual reality, others add social layers to video chat or build 3D environments on top of existing platforms like Second Life or Microsoft’s AltspaceVR .
During the pandemic, revamped developer conferences and trade shows have been able to port keynote addresses or panels to a Zoom format fairly seamlessly, but there are plenty of elements of the Burning Man experience that the teams involved realize might be impossible to replicate with online platforms. The developers creating the event’s virtual worlds are determined to rethink the conventions of online social networking to ensure that Burners make new friends this year.
“The sense of awe and scale is tricky,” says Ed Cooke, who is building one of the official apps. “One way of explaining Burning Man is that it’s a state of mind that you access as a side effect of all the things that happen on the way there.”
Cooke, a London startup founder who also boasts the title of Grand Memory Master, earned for — among other things — memorizing the order of 10 decks of cards in less than an hour, has been building SparkleVerse with his friend Chris Adams, whose daytime gig is as a senior software manager at Airbnb.
Their web app, which pairs a 2D map interface with video chat windows, is primarily focused on advancing how shared context can facilitate and better frame social relationships.
Amid quarantine, the pair tells TechCrunch they have been creating deeply complicated video chat parties for their friends. One example is a moon-themed party where they created a clickable map of the lunar surface that guided the 200 attendees through 16 separate virtual spaces with their own themes. Before the party kicked off, the hosts walked people through the “experience of traveling to the moon” by guiding them through the effects of zero gravity and instructing them to play along with experiencing it. Another hot tub-themed party invited guests to jump into their bath tub before firing up Zoom.
Cooke and Adams are leaning on some of these mechanics to create a Burning Man theme, hoping that taking cues from immersive theatre will enable people to commit more deeply to the experience. The acts of driving, losing your phone connection and growing tired and hungry on the way to the physical event add to a “spaciousness in your consciousness” that allows people to act more freely, Cooke says. He wants participants to replicate these experiences by taking steps outside their normal life in the run-up to the event, whether that’s sitting through an obscenely long video chat session to simulate a drive to the desert or setting up a tent in their living room, or cutting off their water line and avoiding showers during the nine days.
“All of this is embedding you further and further into this distant context, miles away from your normal life, where effectively in the course of this, you’re just becoming a radically less boring person,” Cooke explains in a nine-minute video outlining the platform.
Many of the apps are building on the idea of how spatial interfaces can feed greater social context and make it easier to approach people and make new friends.
Another official app, Build-a-Burn, takes the idea of a stylized 2D interface for video chat even further with a sketched-out grayscale map of Black Rock City that users can navigate little stick figures across. As a user moves through different camps and their avatars get physically close to each other, new video chat screens fade in and users can gain the experience of venturing into a new social bubble.

A screenshot of Build-a-Burn
While Build-a-Burn and SparkleVerse are leaning more heavily on video chat, other experiences hope that creating massive 3D landscapes that match the scale of the real-world event will help people get into the spirit of the event.
Other than Burn2, which is wholly contained within the Second Life platform, most of the 3D-centric apps integrate some level of virtual reality support. Projects that support VR headsets include The Infinite Playa, The Bridge Experience, MysticVerse, BRCvr (which taps into Microsoft’s AltspaceVR platform) and Multiverse.
Each of the VR experiences will also allow users to join on mobile or desktop, an effort to ensure that the apps are more widely accessible.
Over on Extra Crunch, read about how a new generation of chat apps are leaning on game-like interfaces
Multiverse creator Faryar Ghazanfari, who runs an AR startup and previously worked on Tesla’s legal team, says that the motivations for building his app were a bit on the selfish side, telling TechCrunch that he became “extremely sad” after the physical event’s cancellation and felt the need to help build a place where he could reunite with his own camp.


Screenshot from a demo of Multiverse.
Ghazanfari tells TechCrunch he feels a responsibility in creating the environment that other Burners will experience; he says his chief concern is capturing the event’s complexity. Compared to the other apps, Multiverse focuses primarily on providing a photorealistic 3D playground where avatars can zoom around.
“As Burners, we don’t think of Burning Man as just a music festival or art festival; it is much more than that. Burning Man is a social experiment of creating a community out of a shared struggle,” Ghazanfari says.
Each of the Burning Man-approved apps seem to engage with evoking that shared struggle differently, which appears to be the most looming challenge of moving this event to a virtual format. While the apps hope to bring elements of the physical event into their virtual spaces, the creators also seem to realize that aiming to compete with attendees’ past memories is unwise. It’s a challenge that has been faced by dozens of startups in the virtual reality space over the past several years.
“I think the main challenge is taking something that exists in reality and then porting it into a different platform,” said Adam Arrigo, CEO of Wave, a venture-backed startup that initially launched a VR app for music concerts but has since shifted focus to mobile and desktop experiences. “When you’re in these digital spaces, the agency that you have as a user and the experiences you can create are so different than something that could exist, even at a concert.”
Financial uncertainty
Perhaps the biggest unknown, as the organization readies for Burning Man’s August 30 start date, is that nobody really has any idea how many people are going to show up. While Blumenfeld pointed me to suggestions the entire digital event could attract up to 30,000 people over its nine-day run, Ghazanfari hopes that hundreds of thousands or millions of users will come into the fold of his experience.
Another point of contention internally is how exactly the groups plan to monetize these digital experiences.
In 2020, the standard ticket price for Burning Man was $475. The organization postponed the “main sale” of tickets prior to this year’s physical event’s cancellation, but they had already sold tens of thousands of tickets. Ticket holders will have the option of being refunded, but the organization has encouraged those who “have the means” to consider making a full or partial donation of the ticket price instead.
In 2018, Burning Man cost $44 million for the organization to produce, according to tax documents. The Burning Man Project reported about $43 million in ticket sales from that event, with other donations and revenue streams bringing the nonprofit’s total revenue for that fiscal year to about $46 million. In a blog post, the event’s organizers noted that though the group had event insurance, they were not covered for a cancellation caused by a pandemic. Burning Man Project says it has $10 million in cash reserves, but that it anticipates draining through that funding by the end of the year to stay afloat. The organization is listed as having received a loan from the federal government’s Paycheck Protection Program for between $2-5 million.
While some like Ghazanfari are pushing to make their experiences free to access with the option of giving a donation later, others expressed desire for a single digital ticket that would give attendees access to all eight digital experiences. Cooke says users will need to pay a $50 entrance fee to access the SparkleVerse.
The disparate nature of the experience being built this year — with some being shipped as native apps, others in HTML5 and others inside existing tech platforms — meant that a unified ticketing platform just wouldn’t work, Blumenfeld told TechCrunch. Not all of the developers were thrilled with this outcome, which they fear could fracture attendance at events on certain platforms. The biggest concern seemed to be ensuring that all of this effort pays off in some way for the organization so that they can continue to host the Burning Man event post-pandemic.
“One of the biggest reasons we’re all doing this is to help Burning Man survive, because the Burning Man organization unfortunately was really badly hit because of COVID,” Ghazanfari says. “The organization is in kind of a precarious situation financially.”
The organization has attracted criticism in recent years for the event’s inclusiveness. Some of the developers acknowledge that planning for a nine-day trip to the middle of the desert can be daunting and prohibitively expensive for people that want to join the community, and they hope that this year’s shift to a digital format will open up the event to more people and that these apps can be a less intimidating way for skeptics to get a taste of the community.
Thinking of the future
None of the developers behind the digital experiences are being paid for their efforts building these apps. However, the Burning Man Project has given at least some of them perpetual licenses to continue operating these digital platforms with the Burning Man name and an option to monetize, though a percentage of proceeds will be kicked back to the organization.
While getting this event across the finish line by the end of the month is daunting enough, the Burning Man Project is also trying to consider how its rapid learnings will apply to next year, though they hope that the physical event returns for 2021.
Blumenfeld says he plans to spend the next year working on the background infrastructure so that items like gating and ticketing functions for a virtual Burning Man can all be centralized.
While having eight distinct experiences this year could complicate the goal of getting one big group together, developers concerned about troubleshooting their new apps or having a sudden influx of virtual Burners overwhelm their infrastructures view multiple entry points to the festival as a necessary logistical move. Organizers hope the diversity of options will keep things interesting for attendees.
“I think we’ve got a good mix, and part of it is, we want to learn,” Blumenfeld says. “What we’re trying very hard to avoid is being in Zoom meeting hell.”
Whether users are connecting via video chat or as avatars inside a large virtual world, the developers building Burning Man’s virtual experiences believe they are operating on the cutting edge of virtual interaction and that they are rethinking elements of modern social networking to create a virtual Burning Man where people will be able to form new social bonds.
“I’ve fallen in love with this idea that at some point in the future, some Ph.D. student in 300 years time is going to write a thesis on the first online Burning Man, because it does feel like an extraordinary moment of avant garde imagineering for what the future of human online interaction looks like,” Cooke tells TechCrunch.
]]>
TechCrunch
TechCrunch
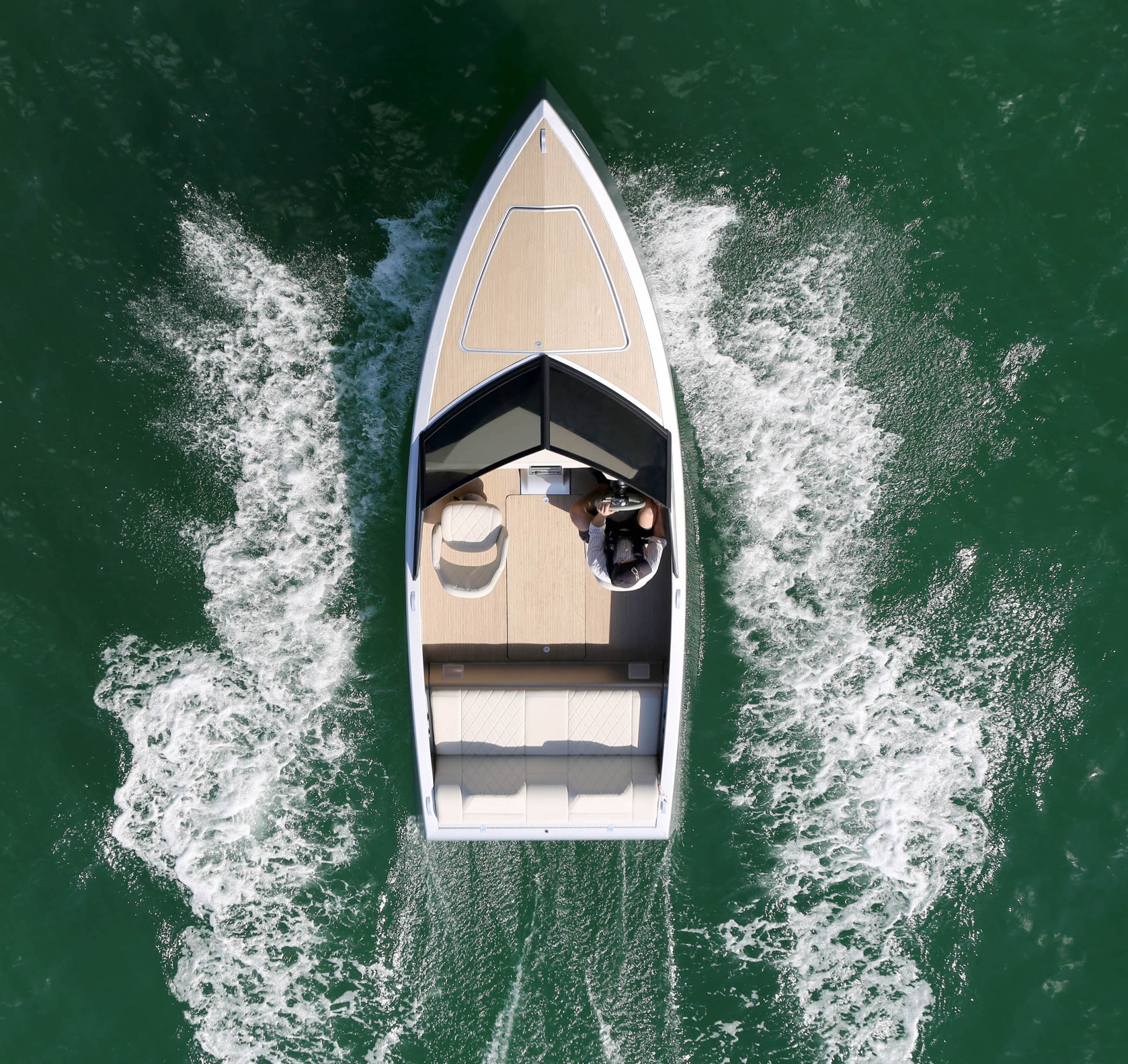
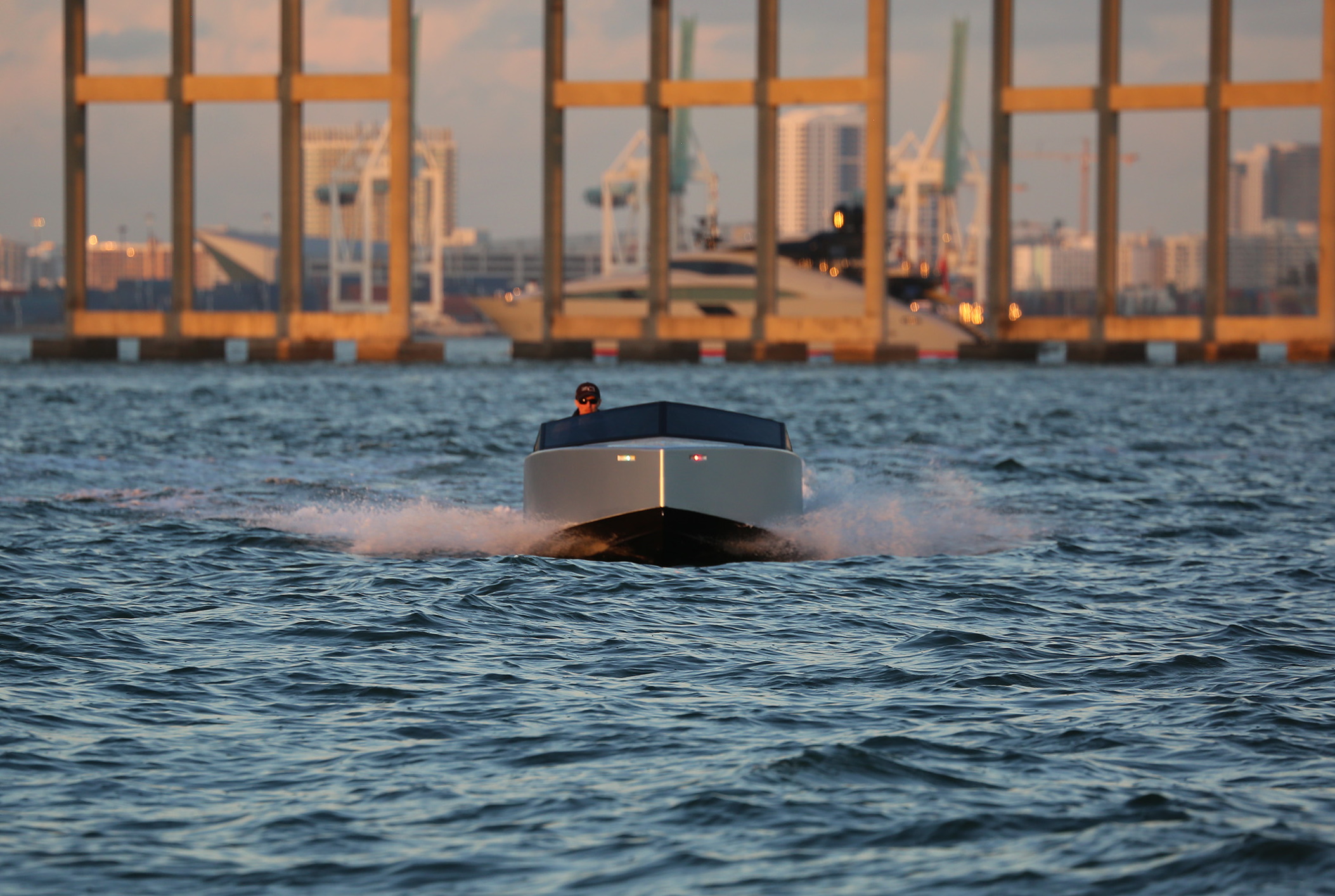
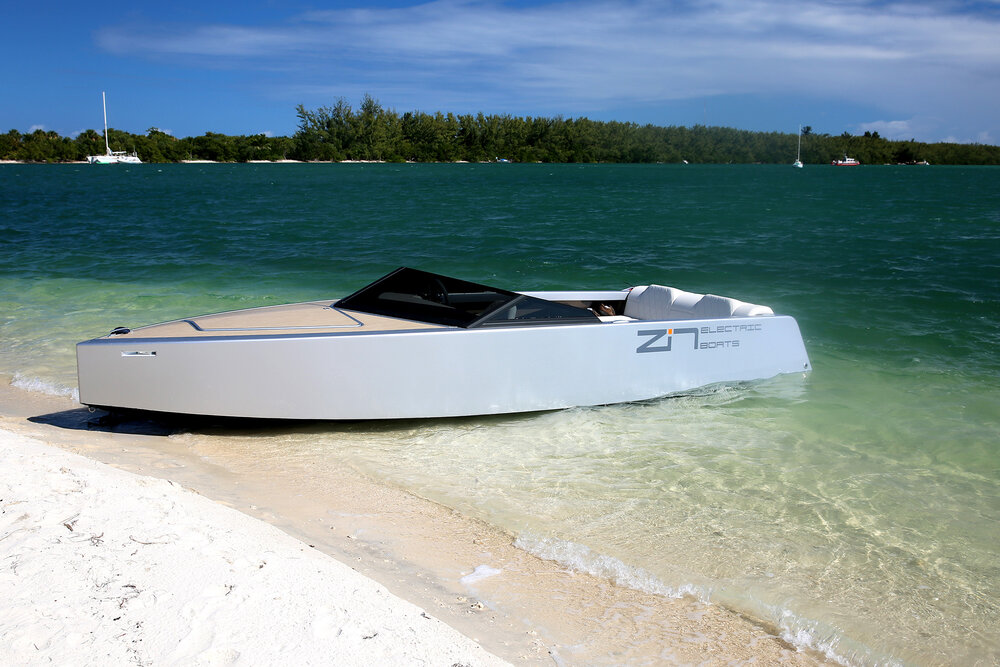
With a minimalist design like a silver bullet, built almost entirely from carbon fiber, the 20-foot Z2R is less than half the weight of comparable craft, letting it take off like a shot and handle easily, while also traveling a hundred miles on a charge — and you can fill the “tank” for about five bucks in an hour or so.
Waiting for the other shoe to drop? Well, it ain’t cheap. But then, few boats are.
Piotr Zin, the company’s namesake, has been designing racing sailboats for 20 years, while working in industrial design at BMW, GM and other major companies. Soon after settling down on a houseboat on Seattle’s Lake Union, he realized that the waterways he had enjoyed his whole life might not exist for the next generation.
(Disclosure: Zin actually moved in next door to my mother, and I happened to find out he was working on this while visiting her.)
“The reason I started working on electric boats specifically is because I had a kid, and I had a come to Jesus moment,” he told me. “I realized: If we’re not going to do something personally about the quality of the water we live in, it’s not going to be here when my kid is my age.”
Illustrious precursors
Traditional gas-powered boats are very much a product of the distant past, like running a ’70s-era car half underwater. Surprisingly, electric boats are equally old. Like electric cars, they enjoyed a brief vogue in the early 20th century. And likewise they were never considered viable for “real” boating until quite recently.
Like most things, it comes down to physics: “The power required to move a boat, versus the power to move a car, is absolutely enormous,” Zin explained. “It’s like driving a car in first gear at full throttle all the time.”
That level of draw limited electric boats to being the aquatic equivalent of golf carts — in fact, carts and some of the more popular old-school electric boats share many components. If you’ve ridden in one, it was probably a Duffy, which has made models for puttering around lakes at 3-4 knots since the ’60s. Perfectly pleasant, but not exactly thrilling.
“We tested this boat to 55, but decided not to sell that to people. It’s just insane.”
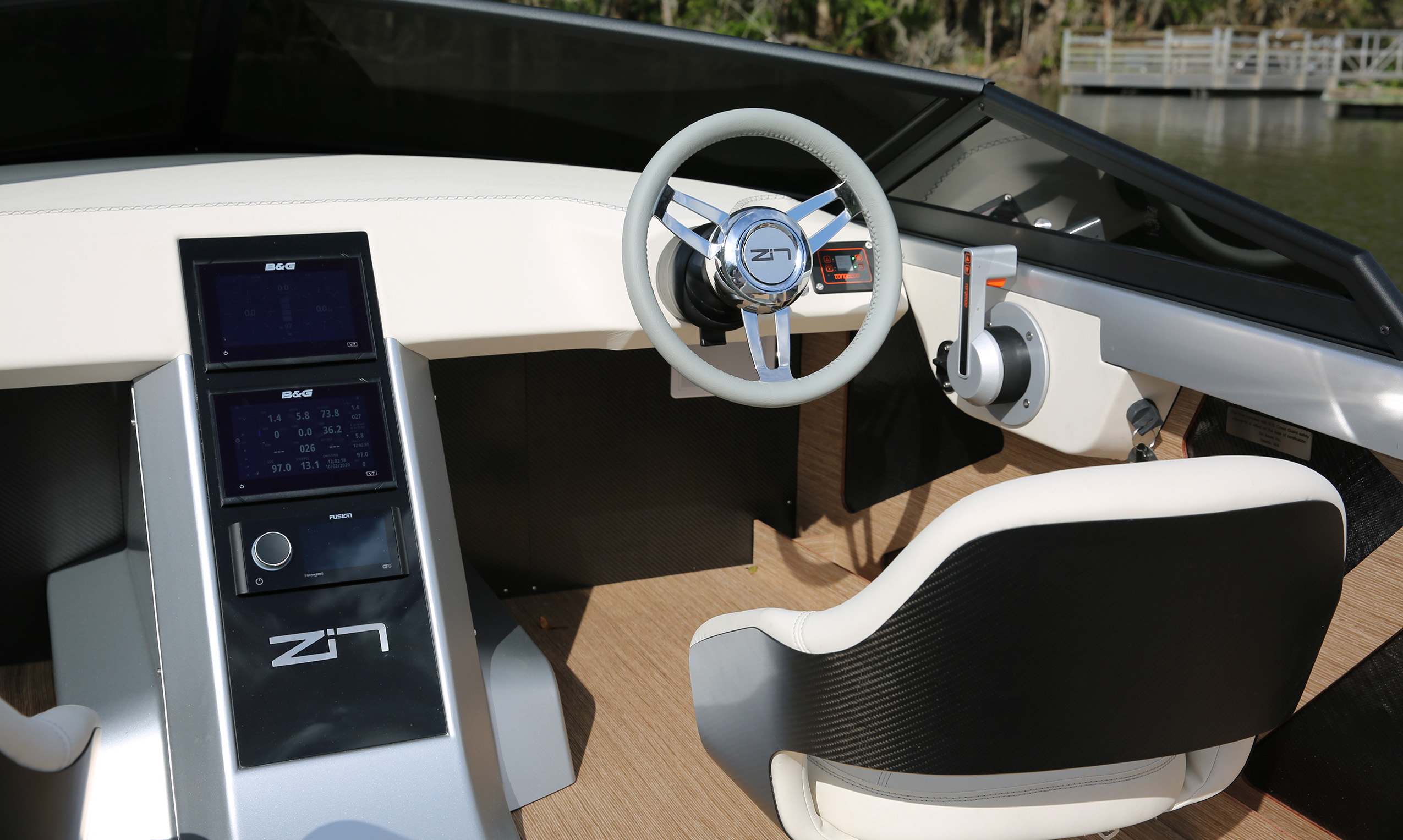
What changed everything was the increasing density and falling cost of lithium-ion batteries. The Z2R uses BMW batteries mated to a custom Torqeedo engine, and at cruising speeds (say 15 knots) can go a hundred miles or more. It recharges using anything from an ordinary wall plug to the high-amperage charging cables found at most marinas, in which case it will put another 50 miles in the tank while you eat a sandwich.
Considering traditional boats’ fuel efficiency and the rising price of marine gas, going electric might save a boat owner thousands every year. (Maintenance is also practically non-existent; Zin advised hosing it down once in a while.)
But it’s also more than capable of going extremely fast.
“The top speed is way over 30 knots,” Zin noted. “We tested this boat to 55, but decided not to sell that to people. It’s just insane.”
Having ridden in it myself, I can confirm that the Z2R really jumps off the line in a level-bottomed way that, compounded by its near silence, seems impossible. Just as Tesla’s consumer sedans compete with Lamborghinis in 0-60 times, the instantaneous response is almost frightening.
“The boat was designed around the battery. The unique part of using an electric system is we can put the motor anywhere we want,” Zin said. By sitting it flat on the bottom, the center of gravity is lowered and weight distribution evened out compared to most speedboats. “You look at a lot of traditional boats’ builds, they kind of cram everything in the back. Then when you put the hammer down, you can’t see anything for five seconds. In this boat, there’s no bow rise — it sits flat.”
Being so level means there’s almost no risk of overturning it, or many of the other failure modes resulting from lopsided designs that misbehave at speed. Simplicity of operation and surprising performance seem to be a family characteristic of electric vehicles.
Design by wire
“Most builders aren’t about innovation, they’re about ‘this is how we do it.’ “
Zin is proud to have designed the boat himself from scratch, using both high-performance fluid dynamics software and scale models to work out the shape of the hull.
“Boat building is a very traditional business. Most builders aren’t about innovation, they’re about ‘this is how we do it.’ ” Zin said. “But there’s a huge advantage in being able to use these tools. The computing power that we have in video cards just in the last few years, mainly because of the gaming industry, has pushed what’s possible further and further.”
Previously, large computational fluid dynamics suites would have users submit their parameters and pick a few milestone speeds at X thousand dollars per data point — 10 knots, 20 knots, etc. The way the water would react to the boat and vice versa would be calculated at those speeds and extrapolated for speeds in between. But with increases in computing power, that’s no longer necessary, as Zin ended up proving to a commercial CFD software provider when he used a separate compute stack to calculate the water’s behavior continuously at all speeds and in high definition.
“Right now you can run the boat [in the simulation] at any speed you want and see the way the water will spray, including little droplets. And then you can tweak the shape of your hull to make sure those droplets don’t hit the passengers,” he said. “It’s not exactly the way most boat designers would do it. So utilizing high-end software that was not really being given its full potential was amazing.”
Building practically everything out of carbon fiber (an ordeal of its own) puts the whole boat at around 1,750 pounds — normally a 20-foot boat would be twice that or more. That’s crucial for making sure the boat can go long distances; range anxiety is if anything a bigger problem on the water than on the road. And of course it means it’s quick and easy to control.
Yet the boat hardly screams speed. The large open cockpit is flat and spacious, with only a steering wheel, throttle and screens with friendly readouts for range, media controls GPS and so on. There’s no vibration or engine roar. No aesthetic choices like stripes or lines suggest its explosive performance. The wood veneer (to save weight — and it’s tuned to the speakers to provide better sound) floor and cream leather upholstery make it feel more like a floating Mercedes.
That’s not an accident. Zin’s first customers are the type of people who can afford a boat that costs $250,000 or so. He compared it to Tesla’s Roadster: A showy vehicle aimed at the high end that will fund and prove out the demand for a more practical one — an open-bow tender model Zin is already designing that will cost more like $175,000.
Conscience with a wallet
The target consumer is one who has money and an eco-conscious outlook — either of their own or by necessity.
“There are a lot of inquiries from Europe, where the environmental restrictions are stricter than in North America. But we also have a number of pristine lakes that are electric-only for the purpose of keeping them clean,” Zin explained. “So if you live on a lake in Montana that’s electric-only, you have the option to go at five knots, and you can’t even cross the lake because the boat is so slow… or you can have a fully functional powerboat that you can water ski behind, the same speeds you get in a gas power boat, but it’s absolutely emissions free. I mean, this boat is as clean as it gets — there’s zero oil, zero gasoline, zero anything that will get into the water.”
It really made me wonder why the whole industry didn’t go electric years ago. And in fact there are a few competitors, but they tend to be even more niche or piecemeal jobs, mating an electric engine to an existing hull and saying it’s an electric boat that goes 50 knots. And it does — for five or 10 minutes. Or there are custom boat builders who will create something quite nice for a Zin-type customer — head on over to Monte Carlo and buy one at auction for a couple million bucks.
Zin sees his boat as the first one to check every box and a few that weren’t there before. As fast as a powerboat but nearly silent; same range but a fraction of the price to get there; handles like a dream but requires practically no maintenance. It’s as smart as the smartest car, limiting its speed based on the waterway, automatically adjusting itself to stay within range of a safe harbor or charger, over-the-air updates to the software anywhere in the world. I didn’t even get a chance to ask about its self-driving capabilities.
As a first-time founder, a technical one at that, of a hardware company, Zin has his work cut out for him. He’s raised seed money to get the prototype and production model ready, but needs capital to start filling his existing orders faster. Like many other startups, he was just gearing up to go all out when the pandemic struck, shutting down production completely. But they’re just about ready to start manufacturing again.
“I realized that there isn’t such a thing as a boat company any more,” said Zin. “Part of what we do is to build that shell that holds everything, and it happens to be moving through the water, which makes it a boat, but that’s really where the boating part of it ends. It’s really a technology hub, and my company is not just a boat company, it has to be a technology company.”
He said that his investors understand that this isn’t a one-off toy but the beginnings of an incredibly valuable IP that — well, with Tesla’s success, the pitch writes itself.
“We don’t only have a plan like, just make one really fast boat,” Zin concluded. “We know what we want to do with this technology right now, we know what we’re going to do with this technology in 24 months, and 48 months; I wish I could show you some of this stuff. It’s tough, and we need to survive this year, but this is just the start.”
]]>







