TechCrunch
TechCrunch
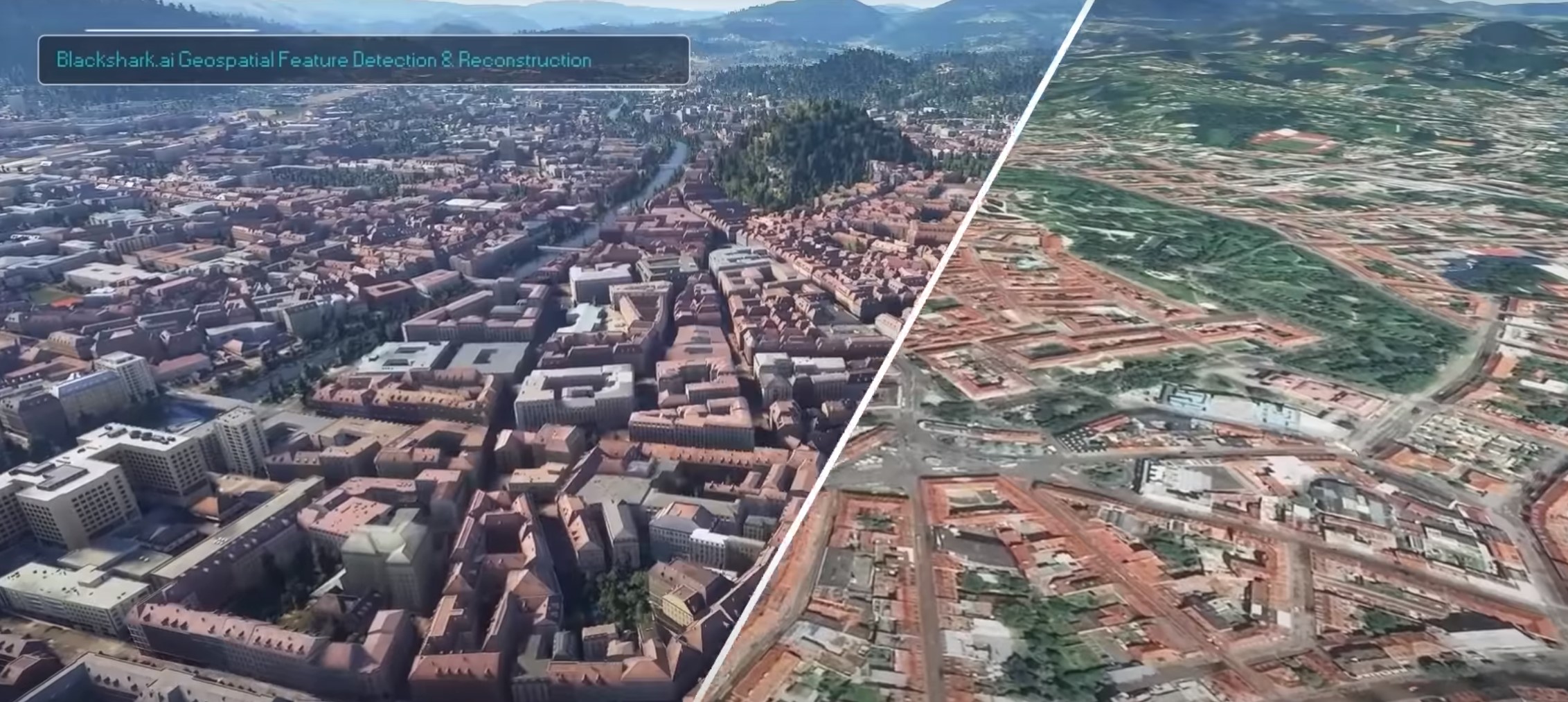
One of those is the small Austrian startup Blackshark.ai from Graz that, with a team of only about 50 people, recreated every city and town around the world with the help of AI and massive computing resources in the cloud.
Ahead of the launch of the new Flight Simulator, we sat down with Blackshark co-founder and CEO Michael Putz to talk about working with Microsoft and the company’s broader vision.
Blackshark is actually a spin-off of game studio Bongfish, the maker of World of Tanks: Frontline, Motocross Madness and the Stoked snowboarding game series. As Putz told me, it was actually Stoked that set the company on the way to what would become Blackshark.
“One of the first games we did in 2007 was a snowboarding game called Stoked and S Stoked Bigger Edition, which was one of the first games having a full 360-degree mountain where you could use a helicopter to fly around and drop out, land everywhere and go down,” he explained. “The mountain itself was procedurally constructed and described — and also the placement of obstacles of vegetation, of other snowboarders and small animals had been done procedurally. Then we went more into the racing, shooting, driving genre, but we still had this idea of positional placement and descriptions in the back of our minds.”
Bongfish returned to this idea when it worked on World of Tanks, simply because of how time-consuming it is to build such a huge map where every rock is placed by hand.
Based on this experience, Bongfish started building an in-house AI team. That team used a number of machine-learning techniques to build a system that could learn from how designers build maps and then, at some point, build its own AI-created maps. The team actually ended up using this for some of its projects before Microsoft came into the picture.
“By random chance, I met someone from Microsoft who was looking for a studio to help them out on the new Flight Simulator. The core idea of the new Flight Simulator simulator was to use Bing Maps as a playing field, as a map, as a background,” Putz explained.
But Bing Maps’ photogrammetry data only yielded exact 1:1 replicas of 400 cities — for the vast majority of the planet, though, that data doesn’t exist. Microsoft and Asobo Studios needed a system for building the rest.
This is where Blackshark comes in. For Flight Simulator, the studio reconstructed 1.5 billion buildings from 2D satellite images.
Now, while Putz says he met the Microsoft team by chance, there’s a bit more to this. Back in the day, there was a Bing Maps team in Graz, which developed the first cameras and 3D versions of Bing Maps. And while Google Maps won the market, Bing Maps actually beat Google with its 3D maps. Microsoft then launched a research center in Graz and when that closed, Amazon and others came in to snap up the local talent.
“So it was easy for us to fill positions like a PhD in rooftop reconstruction,” Putz said. “I didn’t even know this existed, but this was exactly what we needed — and we found two of them.
“It’s easy to see why reconstructing a 3D building from a 2D map would be hard. Even figuring out a building’s exact outline isn’t easy.
“What we do basically in Flight Simulator is we look at areas, 2D areas and then finding out footprints of buildings, which is actually a computer vision task,” said Putz. “But if a building is obstructed by a shadow of a tree, we actually need machine learning because then it’s not clear anymore what is part of the building and what is not because of the overlap of the shadow — but then machine learning completes the remaining part of the building. That’s a super simple example.”
While Blackshark was able to rely on some other data, too, including photos, sensor data and existing map data, it has to make a determination about the height of the building and some of its characteristics based on very little information.
The obvious next problem is figuring out the height of a building. If there is existing GIS data, then that problem is easy to solve, but for most areas of the world, that data simply doesn’t exist or isn’t readily available. For those areas, the team takes the 2D image and looks for hints in the image, like shadows. To determine the height of a building based on a shadow, you need the time of day, though, and the Bing Maps images aren’t actually timestamped. For other use cases the company is working on, Blackshark has that and that makes things a lot easier. And that’s where machine learning comes in again.
“Machine learning takes a slightly different road,” noted Putz. “It also looks at the shadow, we think — because it’s a black box, we don’t really know what it’s doing. But also, if you look at a flat rooftop, like a skyscraper versus a shopping mall. Both have mostly flat rooftops, but the rooftop furniture is different on a skyscraper than on a shopping mall. This helps the AI to learn when you label it the right way.”
And then, if the system knows that the average height of a shopping mall in a given area is usually three floors, it can work with that.
One thing Blackshark is very open about is that its system will make mistakes — and if you buy Flight Simulator, you will see that there are obvious mistakes in how some of the buildings are placed. Indeed, Putz told me that he believes one of the hardest challenges in the project was to convince the company’s development partners and Microsoft to let them use this approach.
“You’re talking 1.5 billion buildings. At these numbers, you cannot do traditional Q&A anymore. And the traditional finger-pointing in like a level of Halo or something where you say ‘this pixel is not good, fix it,’ does not really work if you develop on a statistical basis like you do with AI. So it might be that 20% of the buildings are off — and it actually is the case I guess in the Flight Simulator — but there’s no other way to tackle this challenge because outsourcing to hand-model 1.5 billion buildings is, just from a logistical level and also budget level, not doable.”
Over time, that system will also improve, and because Microsoft streams a lot of the data to the game from Azure, users will surely see changes over time.
Labeling, though, is still something the team has to do simply to train the model, and that’s actually an area where Blackshark has made a lot of progress, though Putz wouldn’t say too much about it because it’s part of the company’s secret sauce and one of the main reasons why it can do all of this with just about 50 people.
“Data labels had not been a priority for our partners,” he said. “And so we used our own live labeling to basically label the entire planet by two or three guys […] It puts a very powerful tool and user interface in the hands of the data analysts. And basically, if the data analyst wants to detect a ship, he tells the learning algorithm what the ship is and then he gets immediate output of detected ships in a sample image.”
From there, the analyst can then train the algorithm to get even better at detecting a specific object like a ship, in this example, or a mall in Flight Simulator. Other geospatial analysis companies tend to focus on specific niches, Putz also noted, while the company’s tools are agnostic to the type of content being analyzed.
And that’s where Blackshark’s bigger vision comes in. Because while the company is now getting acclaim for its work with Microsoft, Blackshark also works with other companies around reconstructing city scenes for autonomous driving simulations, for example.
“Our bigger vision is a near-real-time digital twin of our planet, particularly the planet’s surface, which opens up a trillion use cases where traditional photogrammetry like a Google Earth or what Apple Maps is doing is not helping because those are just simplified for photos clued on simple geometrical structures. For this we have our cycle where we have been extracting intelligence from aerial data, which might be 2D images, but it also could be 3Dpoint counts, which are already doing another project. And then we are visualizing the semantics.”
Those semantics, which describe the building in very precise detail, have one major advantage over photogrammetry: Shadow and light information is essentially baked into the images, making it hard to relight a scene realistically. Since Blackshark knows everything about that building it is constructing, it can then also place windows and lights in those buildings, which creates the surprisingly realistic night scenes in Flight Simulator.
Point clouds, which aren’t being used in Flight Simulator, are another area Blackshark is focusing on right now. Point clouds are very hard to read for humans, especially once you get very close. Blackshark uses its AI systems to analyze point clouds to find out how many stories a building has.
“The whole company was founded on the idea that we need to have a huge advantage in technology in order to get there, and especially coming from video games, where huge productions like in Assassin’s Creed or GTA are now hitting capacity limits by having thousands of people working on it, which is very hard to scale, very hard to manage over continents and into a timely delivered product. For us, it was clear that there need to be more automated or semi-automated steps in order to do that.”
And though Blackshark found its start in the gaming field — and while it is working on this with Microsoft and Asobo Studios — it’s actually not focused on gaming but instead on things like autonomous driving and geographical analysis. Putz noted that another good example for this is Unreal Engine, which started as a game engine and is now everywhere.
“For me, having been in the games industry for a long time, it’s so encouraging to see, because when you develop games, you know how groundbreaking the technology is compared to other industries,” said Putz. “And when you look at simulators, from military simulators or industrial simulators, they always kind of look like shit compared to what we have in driving games. And the time has come that the game technologies are spreading out of the game stack and helping all those other industries. I think Blackshark is one of those examples for making this possible.”
]]>
TechCrunch
TechCrunch
Meanwhile, Pinterest employees reached their breaking point when former COO Françoise Brougher sued Pinterest alleging gender discrimination and wrongful termination. Now, they’re demanding systemic change at the company in light of the latest allegation of discrimination.
Gig Life
Uber and Lyft say they’ll have to temporarily pause operations in California
A lot happened with Uber and Lyft this week, so let’s break down exactly what transpired. But first, a quick recap of the events leading up to Uber threatening to cease operations in California.
January 1, 2020: Assembly Bill 5 becomes law. The bill, first introduced in December 2018, codified the ruling established in Dynamex Operations West, Inc. v Superior Court of Los Angeles. In that case, the court applied the ABC test and decided Dynamex wrongfully classified its workers as independent contractors. According to the ABC test, in order for a hiring entity to legally classify a worker as an independent contractor, it must prove (A) the worker is free from the control and direction of the hiring entity, (B) performs work outside the scope of the entity’s business and (C) is regularly engaged in an “independently established trade, occupation, or business of the same nature as the work performed.”
May 2020: California Attorney General Xavier Becerra, along with city attorneys from Los Angeles, San Diego and San Francisco, filed a lawsuit asserting Uber and Lyft gain an unfair and unlawful competitive advantage by misclassifying workers as independent contractors.
The suit argues Uber and Lyft are depriving workers the right to minimum wage, overtime, access to paid sick leave, disability insurance and unemployment insurance. The lawsuit, filed in the Superior Court of San Francisco, seeks $2,500 in penalties for each violation, possibly per driver, under the California Unfair Competition Law, and another $2,500 for violations against senior citizens or people with disabilities.
June 2020: Becerra and others file a motion for a preliminary injunction seeking to force Uber and Lyft to immediately classify their drivers as employees.
August 6, 2020: California Superior Court Judge Ethan P. Schulman hears arguments pertaining to the preliminary injunction. At the hearing, Uber and Lyft maintained that an injunction would require them to restructure their businesses in such a material way that it would prevent them from being able to employ many drivers on either a full-time or part-time basis. Uber and Lyft’s argument, effectively, is that classifying drivers as employees would result in job loss.
“The proposed injunction would cause irreparable injury to Lyft and Uber, and would actually cause massive harm to drivers and harm to riders,” Rohit Singla, counsel for Lyft, said at the hearing.
For example, Lyft estimates it would cost hundreds of millions of dollars simply to process the I-9 forms, which verify employment eligibility. It doesn’t cost anything to file that form, but it would require Uber and Lyft to further invest in their human resources and payroll processes.
August 9, 2020: Judge Schulman grants the preliminary injunction, which goes into effect on August 20, 2020.
“The Court is under no illusion that implementation of its injunction will be costly,” Judge Schulman wrote in the order. “There can be no question that in order for Defendants to comply with A.B. 5, they will have to change the nature of their business practices in significant ways, such as by hiring human resources staff to hire and manage their driver workforces.”
Meanwhile, Uber and Lyft made clear their respective plans to file emergency appeals.
August 12, 2020: Uber CEO Dara Khosrowshahi says Uber will have to temporarily shut down in California if the court doesn’t overturn the preliminary injunction. Lyft says it, too, will be forced to temporarily cease operations in California.
August 13, 2020: Judge Schulman denies Uber and Lyft’s appeal. Uber says it plans to file another appeal, while Lyft says it will seek a further stay from the state’s appellate court.
Looking ahead
August 20, 2020: Preliminary injunction is set to go into effect and Uber and Lyft will likely be temporarily ceasing operations in California.
November 2020: Californians will vote on Prop 22, a ballot measure majorly funded by Uber, Lyft and DoorDash. Prop 22 aims to keep gig workers classified as independent contractors. The measure, if passed, would make drivers and delivery workers for said companies exempt from a new state law that classifies them as W-2 employees.
The ballot measure looks to implement an earnings guarantee of at least 120% of minimum wage while on the job, 30 cents per mile for expenses, a healthcare stipend, occupational accident insurance for on-the-job injuries, protection against discrimination and sexual harassment and automobile accident and liability insurance.
Stay Woke
Pinterest’s fall from grace
Back in 2015, Pinterest was known as one of the companies doing some of the best work around diversity, equity and inclusion. That perception changed this year.
Pinterest was one of the first tech companies to set concrete hiring goals. In 2015, those goals were to increase hiring rates for full-time engineering roles to 30% female; increase hiring rates for full-time engineers to 8% from underrepresented ethnic backgrounds; increase hiring rates for non-engineering roles to 12% underrepresented backgrounds; and implement a Rooney Rule requirement where at least one person from an underrepresented background and one female candidate is interviewed for every open leadership position.
Pinterest was also one of the first companies to hire a head of diversity and inclusion. In 2016, Pinterest hired Candice Morgan for the role. Morgan left the company earlier this year and joined VC firm GV as its equity, diversity and inclusion partner. Still, Morgan had one of the longest stints at any tech company’s diversity and inclusion department.
In the company’s 2020 diversity report, Pinterest showed it beat all of its hiring goals, but what was missing from that report was retention data. When TechCrunch asked in January if they would make the data available, a Pinterest spokesperson said, “unfortunately, we can’t share the retention metrics publicly, but it will continue to be an internal priority.”
Now, transparency about retention data is just one of a handful of demands Pinterest employees have. Two days ago, former Pinterest COO Françoise Brougher sued the company, alleging gender discrimination, retaliation and wrongful termination. Prior to that, Aerica Shimizu Banks and Ifeoma Ozoma, also accused Pinterest of discrimination.
In light of those allegations, Pinterest employees are walking out today to demand change at the company. The walkout is directly in response to recent accusations of racial and gender discrimination at Pinterest. In addition to the walkout, there’s a petition circulating throughout the company demanding systemic change. The change they seek entails full transparency about promotion levels and retention, total compensation package transparency and for the people within two layers of reporting to the CEO to be at least 25% women and 8% underrepresented employees.
Don’t Miss
Triplebyte incubates ColorStack to increase Black and Latinx representation in CS programs
A beginner’s guide to diversity, equity and inclusion
]]>