TechCrunch
TechCrunch
There is, of course, a kind of serendipity in today’s launch of Fitness+. While Apple gets points for general prescience, one assumes the company wasn’t privy to any better information than the rest of us, and certainly couldn’t have predicted how radical a shift the exercise industry would undergo over the past nine months.
Most of the information on COVID-19’s impact on gyms is, at best, either myopic or anecdotal, but there seems little doubt the industry has been — and will continue to be — radically impacted by the pandemic. “Devastated” might be a more accurate term. After all, it’s mid-December as I’m writing this and many are still scared to venture back into a business that routinely ranks among the highest risk for the virus’s spread. As if people needed another excuse to skip daily workouts.
What we can say for certain, however, is that Wall Street and Silicon Valley cultures have reacted, big time. In late-June, Lululemon purchased Mirror for a jaw-dropping $500 million. Shortly after, Bank of America started tossing out predictions, noting the guided workout company could generate $700 million and hit 600,000 subscribers by 2023. Peloton stock hit a slight blip with Apple’s Fitness+ launch announcement last week, but otherwise, it’s a been a terrific year from the home treadmill/stationary bike maker.
None of this is to say, of course, that these companies weren’t already doing gangbusters, but the pandemic has certainly — in the words of an overzealous fitness instructor — kicked it up a notch. Yes, I grimaced a bit as I wrote that last sentence, but ultimately, what is a fitness class if not an exercise in swallowing one’s pride?
My own experience with group workouts is limited. Prior to the pandemic, I went to the gym five to seven days a week. When on a work trip, I would be the weirdo at the hotel gym, trying to figure out how to change the one giant-tube television from Fox News at 6AM. I don’t care what your political leanings are — no Fox and Friends for me before coffee and a run.
Since the pandemic, my options have been…limited. In addition to the harrowing COVID fallout in my home of Queens in March/April, I dealt with some of my own health complications that severely limited my workout options. I’ve weaned myself back into a kind of makeshift workout regimen in the intervening few months — first through some YouTube yoga and now through five to 15-mile daily walks.
It’s an improvement. And I’m counting my blessings and all of that, knowing well that as bad as things had and have gotten, they ultimately could be worse. Truth is, though, like many Americans (and non-Americans, no doubt), the cost-benefit analysis of going back to the gym still doesn’t make a heck of a lot of sense for me. Given the space constraints of my New York City apartment, however, neither does a Peloton.
I do, however, have an Apple Watch. And a yoga mat. And just about enough space in my bedroom to make this work. I’ve been at this for a few days — doing a couple of workouts a day, ranging from about 10 to 20 minutes a piece. Like Matthew did last week with his AirPods Max writeup, I’m going to opt not to call this a “review.” It’s not fair to the product and — more to the point — it’s not fair to you, the reader.
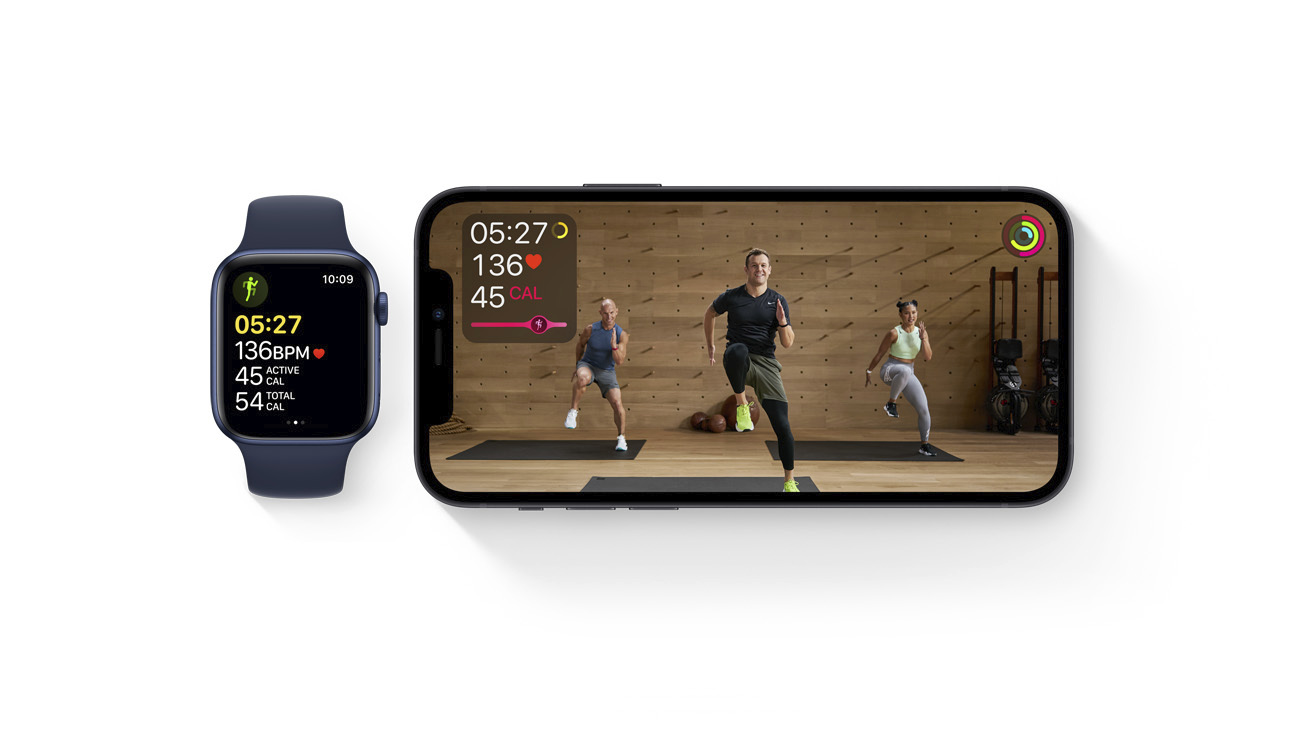


Image Credits: Apple
What I can say definitely, however, is that I do plan to continue using the service beyond these first few days. Perhaps that’s a testament to the product’s potential. Or maybe it’s just a sign that I’m looking for a way to stop feeling like a wet garbage bag full of room temperature cottage cheese all of the time. The truth, as usual, probably lies somewhere in the middle.
Fitness — like anything health related — is a highly personal thing. There has never and likely will never be a kind of one-size-fits-all solution to the problem of working out. And while Fitness+ is the latest, shiny attempt to tackle the issue, that’s certainly the case here as well. The best I can do for you right now is discuss my own personal needs and experiences. Some will likely sound familiar, others not.
My biggest fitness hurdles are: time and space. The time bit should be self-explanatory — and familiar to most. Even during a year-long quarantine, there’s somehow never enough of the stuff. Space is mostly — but not entirely — a side effect of my decision to live in New York City on a journalist’s salary.
There’s also the matter of variety. Once I find something I like at a particular restaurant, I will continue to order it until I’m sick of it. And that likely won’t be for a while. That’s usually the case with how I work out as well (likely to the detriment of my overall health). Once I discovered that I could tolerate running (and keep the pounds off doing it), I ran until I messed up both of knees.
As I said above, walking long distances across bridges and into different boroughs has been a small but important respite for me during hell year. In doing that, I’ve pretty consistently closed my Apple Watch rings (“Stand” can still be a stickler on work days). But while I generally don’t have an issue hitting those goals, switching up how I can get there has been something of a challenge.
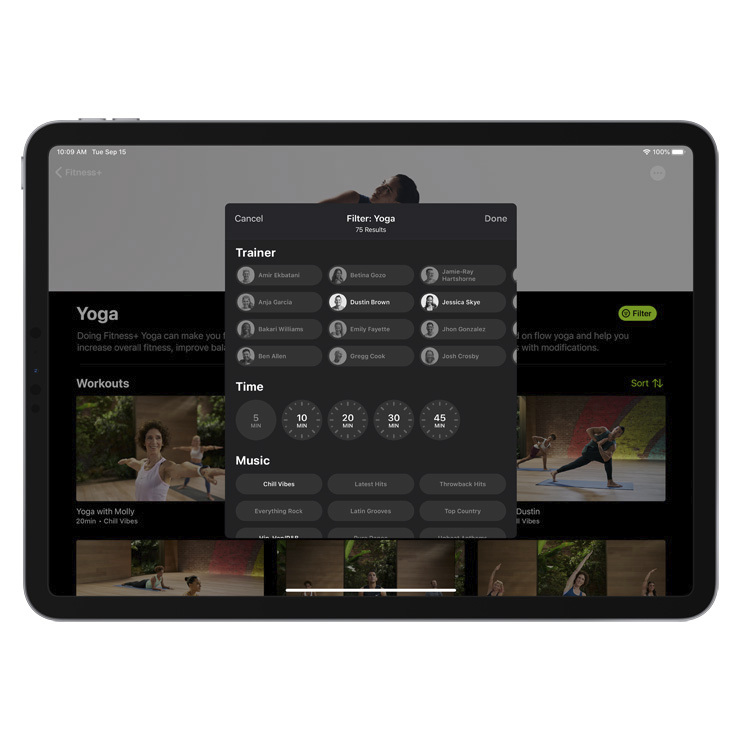

Image Credits:
Fitness+ does offer some key benefits right off the bat. The first — and arguably most important — is convenience. For $10 a month, you get whatever peace of mind comes with knowing that every Monday, Apple is going to drop a new crop of new workout videos for you every week. That content can be accessed across a number of Apple devices. Namely: the iPhone, iPad and Apple TV.
Another thing you should probably know about me (you’re learning all sorts of fun stuff today, right?) is that I’m one of those no TV weirdos, and therefore my own experiences are limited to the iPad and iPhone. There are a number of reasons to go for the Apple TV in this setup, but the most important of all, to be honest, is sheer screen real estate. I found the iPad Air’s 11-inch display was totally acceptable in close range, however.
The iPhone was a lot trickier, on the other hand, when it comes to following the trainers. The upshot of both of these, however, is flexibility. That’s a nice feature when it comes to moving between standing and sitting exercises. The other big upshot will come when we all start traveling again. I can certainly see the appeal of busting out one or two of these workouts in my hotel room, instead of gambling that the elliptical machine will be up and running (about 50/50 in my experience).
For now, at least, Fitness+ doesn’t have its own standalone app. Like other premium services before it, Apple’s snuck it into an update of an existing app — a move that ensures the new paid offering is instantly available on millions of devices starting today. In the iPhone app, it appears as one of three tabs. It always felt a little superfluous to have individual apps for Fitness, Health and Watch, but I suppose that now we know why they’ve kept those things separate. Today also marks the arrival of the standard Fitness app for iPadOS, where Fitness+ is more or less the entire experience.
The Apple Watch is required for the Fitness+ experience. There’s apparently a way to circumvent things if, say, you accidentally forgot your Watch at home or your battery dies or what have you. But on the whole, no watch, no Fitness+. Ecosystem’s gonna ecosystem, friend.
The necessity for this particular piece of hardware makes sense when you consider how deeply integrated it is. The Watch really is the core of the Fitness+ experience. It does its usual job collecting your metrics, which are now also displayed for you in real time on screen as you work out. The primary information at the ready is how far you are into the activity bar and your heart rate — the latter in particular seems like an important piece of information for many. And it is pretty fascinating to watch your numbers climb and drop between intervals.


Image Credits: Apple
Honestly, the Apple Watch integration is probably the best-executed aspect of the entire undertaking — down to the way the wearable doubles as a start and stop button for the workout. It also ensures a more complete rundown of your workouts at the end of the day. The truth of a wrist-worn monitor — whether Apple wants to admit it or not — is that it can be hit or miss with full body workouts.
That’s a big part of the reason why the device asks you to start or confirm workout types during normal usage. Give the current sensor technology available for these products, there’s a limit to how precisely you can measure movement. If you’re wearing the Watch and doing pre-selected Fitness+ workouts, on the other hand, the system is able to offer a more complete picture. Collected data is also aggregated into a “Burn Bar,” which will show you roughly where you rank compared to others who have done the exercises (I generally found myself somewhere in the middle). This can be toggled off if you’re not feeling competitive.
Beyond that, there’s really not much in the way of gamification here. The closest Apple’s hand-selected trainers come is the fairly regular encouragement to “close your rings.” It’s tough to strike the balance of motivating without overwhelming. Go too far in either direction and you risk losing people. I’d say on the whole Apple does a decent job striking the balance, down to the fact that there are often three trainers in the videos, each showing you a different level of intensity for the on-screen exercises.
One key thing Apple does lose here, versus both in-person fitness classes and live-streamed ones from the likes of Peloton, is instant feedback. The company has positioned its “on-demand” approach as a way of letting users complete courses at their own pace. In a more ideal world, however, there would be some combination of the two. Apple certainly has the resources to do both — though there’s a fair bit more that goes into live-streaming with real-time bio feedback.
If I had to venture a guess here, I would say that in all likelihood Apple will add live classes at some point. There’s value in having a set appointment you feel obligated to attend. And for all of the Fitness+ trainers’ encouragement that “you’re doing great,” let’s be real: they’re speaking to a camera in a studio for a video that was recorded days — if not weeks — ago.
YOU HAVE NO IDEA HOW I’M DOING!
The variety of exercises on offer is pretty good. I’ve mostly been alternating between Core and HIIT (high intensity interval training). Given that it’s all right there in front of me, I have found myself trying some new stuff. Turns out I still hate dancing in basically all of its forms — but it’s nice to check in every decade or so. The biggest limitation for me (beyond those outlined above) is equipment.
I don’t have a stationary bike or treadmill. I have a kettlebell, but not a complete weight set. I do have a yoga mat, however, which is probably the most common piece of equipment here. Honestly, if you’re thinking of trying Fitness+, I would shell out $25 for a yoga mat. Turns out you can still use it even if you cancel your account. There’s a small description letting you know what equipment is needed below the video. It would be great if Apple added an easie way to filter by equipment, though, given the percentage of workouts that require something.
Ditto for music. Apple really prides itself on the music choices here (and the trainers seems encourage to talk a lot about it). In fact, each course includes an Apple Music playlist of the song choices (ecosystems for the win). I recognize that music choices are every bit as personal as fitness needs, so I know I’m not speaking for everyone when I say the music is, on a whole, mostly bad. As you’d expect.
There are exceptions for different trainers and different exercises, but the selections I mostly encountered in my workouts are more or less the same sort of high energy Top 40 crap you’ve probably already encountered at your gym. If that’s your thing, cool. If not, you’re going to find the alternatives fewer and farther between. I would love if Apple eventually adds an option to toggle off the music or replace it with your own stuff. You can filter by genre within a given exercise category, but for obvious reasons, that’s going to limit the workout selections in the process.
Once you’ve completed a course, a small checkmark will show up in the corner. It sticks around, which is nice if you find something you like, but it would be great if the app more dynamically cycled through things and offered quick reference for what you’ve already done. Again, this is all coming from someone who’s done six or so workouts over three or so days. The app adds customization the more you use it, and I just haven’t been using it long enough.

Image Credits: Apple
The overall execution is about as polished as you’d expect from an Apple production, down to the fact that the trainers were taught some sign language for greetings and goodbyes (in addition to closed captioning). Money has been spent on production value and hiring a diverse group of trainers. And certainly you’re getting more consistent quality here than you would just perusing YouTube for random exercises.
Is it worth $10 a month (or $80 a year), though? My main hesitation on that front is that it’s yet another in a seemingly endless pile of monthly fees from the ever-growing subscription economy. It’s significantly cheaper than a gym, obviously. Though the equipment here is very much bring your own, in the case of Apple, and the Watch doesn’t take the place of in-person feedback from classes or even the kind offered on some of the full-body fitness mirrors.
Like I said at the top I plan to keep using the app for the timing being. I’m still wary of the gym and am generally averse to working out in front of others. And thankfully, I live on the first floor, so none of my neighbors are any the wiser about all of the weird jumping around I’ve been doing lately (though my rabbit finds it amusing).
Here in the States, at least, it seems a safe bet we’ve got at least another four, maybe five months of this pandemic left to deal with. For Apple, that means a solid opportunity to get people on board with its new service. For me, it probably means at least that much more time doing squats in front of an iPad — especially as we’re heading into some truly cold months here on the eastern seaboard. I’ll probably check in my progress in a few weeks or months and maybe feel more comfortable calling it a proper review.
Beyond that, it’s hard to say.
]]>
TechCrunch
TechCrunch
The Harvard professor who wrote the defining book on surveillance capitalism has become the latest voice raised against the $2.1 billion data+devices deal — that’s now been delayed at the regulatory clearance stage for more than a year.
Others calling for the Google-Fitbit acquisition to be blocked — unless or until robust competition, democratic and human rights safeguards can be baked in — include Amnesty International; scores of consumer, privacy and digital rights groups across civic society; and the EU’s very own data protection advisor, to name a few.
EU regulators are still considering whether or not to greenlight the merger. The deadline for them to make up their minds was recently extended into early 2021 — although a decision could come as soon as next week.
Back in August, the Commission opened an in-depth investigation into the deal — saying it was concerned it would “further entrench Google’s market position in the online advertising markets by increasing the already vast amount of data that Google could use for personalisation of the ads it serves and displays”.
EU lawmakers have also expressed skepticism over initial concessions offered by Google which suggested storing Fitbit data in a silo that it said would be kept separate from other Google data.
It also said it would not use Fitbit data for ad targeting — at least for a time-limited period (though it’s not clear what exactly it has proposed in Europe). Elsewhere, Australian regulators are also still eyeing the deal — and recently sought industry feedback on a pledge by Google not to use Fitbit data for ads for 10 years.
The ACCC published draft undertakings in November which includes stipulations such as: “Google must not use any Measured Body Data or Health and Fitness Activity Location Data in or for Google Ads” and that data must be kept separate.
But Zuboff’s point is that targeted advertising is just the tip of the vast data-extracting ambitions of surveillance capitalists — while health data is one of the few personal data fields these digital giants have not yet been able to mine in their usual limitless way.
“Any notion of approving the Fitbit acquisition — based on Google’s promises not to do something that is anyway an irrelevant thing, to do or not to do — is a serious mistake,” she said yesterday, giving the keynote speech at the annual lecture of the EU Parliament’s Science and Technology Options Assessment (STOA) panel.
“Such a decision should be reconsidered immediately. And never again repeated,” she added.
A Google spokesman declined to comment on Zuboff’s remarks — pointing only to its blog post from August where it claims the deal is about “devices not data”.
Beware the “epistemic coup”
In the STOA lecture, Zuboff articulates a view of tech giants’ uncontrolled extraction and use of data leading to what she described as an “epistemic coup” — where bottomless digitally-enabled data extraction leads to an unprecedented dominance of knowledge by the private sector, generating radical inequalities and full-spectrum harms, as a data-empowered few are able to run roughshod over humanity, democratic values and the rule of law in the name of increasing their profits.
“There is no ‘attention economy’; these are effects of a deeper cause — and that cause is surveillance capitalism’s economic imperatives. These corporations are not publishers, they are not distributors, they are not merely adtech providers; they are indiscriminate, radically indifferent all-you-can-eat extractors of everything forever, all for the sake of prediction that become more lucrative as they approach certainty,” she said.
“Knowledge at this kind of scale produces a new kind of power over people. This is what data scientists call the shift from monitoring to actuation. Where there’s actually sufficient data about a machine system to be able to control it remotely. The thing is now it’s not just the machine systems; it’s the human systems.”
The wide-ranging keynote is well worth watching in full for how clearly Zuboff articulates why allowing corporates to “unilaterally claim[…] private human experience for raw material, bent to the purposes of datafication, computational production and sales” is terrible for humanity and the (genuine) communities which make up our civilization — likening it to how uncontrolled extraction of oil for corporate profit has threatened the survival of life on earth, fuelling climate change, biodiversity decline and mass species extinction.
The nub of the argument is that surveillance capitalism’s target is human nature itself — with Zuboff calling out the “data business” playbook of “hidden extraction mechanisms” which she said are robbing us of the ability to fight back.
“Today our nemesis is not, and could never be, mere data or technology — but rather the extractors, led by a handful of giant corporations: Google, Facebook, Apple, Amazon, Microsoft, to name only the largest, along with their complex, far-reaching ecosystems, these are corporate institutions that have pioneered a new logic of extraction but with a dark and startling twist… These corporations have placed the defence of their narrow economic self-interest above the interests of individual sovereignty, democracy and humanity itself.”
The keynote included a call to action to European lawmakers to step in and reverse what has been allowed to become entrenched at humanity’s expense.
“I am here today because the European Union represents humanity’s best hope to alter this course before lawless, unprecedented computational concentrations of knowledge and power become as irreversible and poisonous to our societies as the toxic concentrations of carbon dioxide in our atmosphere have become to our earth,” said Zuboff, adding: “The idea that we could bequeath both of these cataclysms to our children is intolerable.”
EU lawmakers are on the cusp of unveiling a major package of legislative proposals which will update rules for digital services and bring in new requirements for platforms with significant market power.
The Commission’s Digital Services Act (DSA) and the Digital Markets Act (DMA) proposals are due to be presented next Tuesday — the start of a long road of negotiating to turn the policies into EU law.
It has turned out to be particularly awkward timing for the Commission, in parallel with the Google-Fitbit decision. Not least because a key EVP involved in shaping the new digital strategy, Margrethe Vestager, is also the competition commissioner — so she’s simultaneously tasked with deciding whether to waive the tech giant’s latest data acquisition through, even as she puts the finishing touches on ex ante rules for gatekeepers that won’t likely come into force for years.
Vestager told the EU parliament’s Committee on Economic and Monetary Affairs this week that the Commission’s incoming proposals for a major overhaul of digital regulations are necessary to tackle the challenges of the platform economy.
The scale and the scope of the platform economy is “unprecedented and it’s increasing”, she said, acknowledging that the digitization process has “given us a concentration of data, intellectual property, capital — and because of that there’s a lot of power in the hands of a few global players”.
That in turn is making it “really urgent” to complement existing EU competition law enforcement with dedicated regulation for digital services and platform giants, said Vestager.
“The DSA will propose a clear set of due diligence obligations and operate the e-commerce framework for all Internet services within the EU and the point is to ensure that digital services face no borders within the EU, define clearer responsibilities and accountability for online platforms such as social media and marketplaces,” she told MEPs — saying the overarching aim is to ensure consumers have the same protections online as they already do offline.
The aim of the DMA — and its incoming list of “dos and don’ts” for platforms that the EU will define as gatekeepers — is to make sure digital markets “stay open and contestable”, and thus to serve consumers in “the best possible way”.
‘Trust but verify’ via audit authority
In her keynote, Zuboff suggested EU regulators should follow two key principles as they consider what to do.
Firstly, “trust but verify” is how to treat with surveillance capitalists — so no more “taken at face value” pledges swallowed naively and later regurgitated under the one-way logic of extraction maximization. (She raised the awkward example of Facebook’s reversal of an earlier pledge to EU regulators not to combine WhatsApp user data with Facebook data.)
“Secondly we have to keep in mind so often we reduce the harms back to that originating context of targeted advertising — when in fact this whole economic logic has moved way beyond targeted advertising to many other markets,” she also said, warning against EU regulators taking too narrow a view on any concessions made by Google as it works to push open another data gate.
We’ve reached out to the Commission for comment on Zuboff’s remarks.
Zuboff also spoke to concerns that EU regulators don’t believe they have legal grounds to deny Google-Fitbit.
“If the decision to approve Google’s acquisition of Fitbit was made because of a determination that EU laws are not strong enough to defend the acquisition denial in the European courts then let us please stop talking this minute; let’s suspend our event while the parliament moves into an emergency session to pass new laws that are strong enough to take this kind of rejection through the courts. Because we need those laws,” she said.
It would certainly be ironic if the Commission green-lit the Google-Fitbit merger because it was worried about losing a legal challenge down the line — given how frequently tech giants resort to legal action to try to thwart the application of existing EU regulations. Not to mention how fiercely these giants lobby against any new regulation or legislative proposal that would dare to put limits on their ability to continue maximizing their data extraction.
Zuboff said the forthcoming DMA “is the legal instrument to accomplish this necessary lawmaking [against the surveillance capitalists]”, addressing her remarks to those in the EU who have the power to pass laws.
“Make no mistake: This is your opportunity to make a bold intervention to defend democracy against the surveillance capitalists. Faint heartedness is not an option,” she said, adding that the DSA is likewise an essential intervention to defend democracy.
“This is your chance to finally pry open the black box of surveillance capitalism and demand the right of democratic societies to control their own destiny,” she said, suggesting regulators’ watch word here should be “audit authority”.
Democracy must have audit authority to protection the public just as regulators have done in countless other industries, she added.
The Google-Fitbit acquisition was raised in a question to Vestager yesterday during a session of the Committee on Economic and Monetary Affairs — where she was asked what the EU intends to do vis-à-vis health data and competition, given the risk of tech giants gleaning far deeper and more intimate knowledge of users than they’ve been able to via current data-mining practices.
Vestager told the committee she couldn’t comment on the specific merger as the process is ongoing but she said she agreed health data “are much more precious and much more sensitive” than other types of commercially exploited data.
“This is why one has to be very careful when it comes to health data and advertising — because here it can be a much more vulnerable position for the person in question,” she said.
“For health data as such I think it’s very important that the market develops because the more health data that becomes available the more services people expect for the market to provide for them to have a better understanding of how their health develops,” she went on, adding on Google-Fitbit specifically that “it remains to be seen how the remedies were to bear out if they were to be accepted”.
U.S. versus EU approach to antitrust
During the session Vestager also faced a number of questions from MEPs about the difference of approach to antitrust between the EU and the U.S. — where states have just opened a massive antitrust case against Facebook.
She repeatedly stressed that Europe has a “different” approach to competition law versus the U.S., sounding a tad on the defensive.
“The U.S. Facebook case is a different approach than what we have. In Europe we do not have a ban of monopolies. They have a different legal basis in the U.S. We would say you’re more than welcome to be successful but with success comes responsibility — which is why we have article 102 [against abusing a dominant position],” she said.
“As a last resort in Europe we would also be able to ask our [institutions] to split up companies but then we would also have to prove that this was the only thing to solve a competition problem and I don’t think we have been there yet,” Vestager added.
Responding to other questions from MEPs she described her department as doing its “best” across a number of big tech investigations — pointing it’s recently opened case against Amazon and has others ongoing into Google’s and Facebook’s use of data for advertising.
“We have a couple of ongoing investigations into the Facebook ecosystem — on the use of data from customers and consumers into advertising and how the Facebook marketplace is functioning,” she noted.
“These cases are not as advanced as they are in the U.S. when it comes to Facebook but I find [the U.S. action] very encouraging,” she added, saying it’s a sign that “the global debate about tech dominance has been shifting over the last couple of years”.
Asked about Facebook’s reversal of an earlier promise not to combine Facebook and WhatsApp user data, Vestager said EU regulators had performed an analysis at the time — looking into whether such a move would still allow for competition — and “found there would be room for others services of the same kind”.
There were no follow-up questions in the event format so MEPs were unable to ask whether Vestager believes that analysis was sound or flawed. But it’s not a good look that the EU’s competition authorities were left so wrong-footed on Facebook’s market power.
Off her own bat, Vestager merely said: “It remains to be seen what will be the outcome of the U.S. [Facebook antitrust] case; as I said they have a different legal basis — to see if by acquiring this company you have entrenched monopoly position.”
She was also asked what the Commission intends to do about companies using self-serving tactics to artificially prolong investigations (and thus delay competition enforcement) — such as by procrastinating or handing out requested information only with substantial delay.
Vestager said its approach is to aim to “always try to balance things out” but she argued it’s important to give businesses enough time to respond properly even though it extends the length of investigations.
During the session she did also note that the aim for the DMA is to enable competition authorities to be “so much quicker” — because the ex ante rules will bake in “self-executing obligations”.
The gatekeeper status also means regulators will not need to do the work of establishing dominance first — “which means you’ll get to the sanction must faster and should prevent damages in the marketplace”, she noted.
It’s not clear whether or not the forthcoming legislative package will feature a new competition tool for specifically tackling digital markets — which the Commission consulted on earlier this year.
Reports have suggested this has been dropped after a standard EU pre-regulatory review process. But the commissioner did not confirm either way.
She was also asked about interim measures — an existing tool she dusted off last year after an extended period when it had not been used, applying it in a case against chipmaker Broadcom.
On this she said the tool has been shown to have been useful — noting the Broadcom case was settled in a year (which is a very speedy turnaround for a competition case) — and she suggested the tool could be used more frequently in the future. “I think that we will see we can use it more often,” she told the MEPs.
]]>


