TechCrunch
TechCrunch
The business world has a love-hate relationship with coaching. Founders are visionaries: They start with an idea, a talent, a dream, but not necessarily the business know-how. Because being an entrepreneur doesn’t require a license or training — Jeff Bezos is an engineer and computer scientist; Elon Musk is an economist and physicist, and so on.
In any other industry, when someone with raw talent — an athlete, a singer, an actor — furthers their career, the first thing they receive is a coach. And it doesn’t stop once they get their first Olympic gold or Grammy.
Coaches don’t leave their side until they hang up their gloves. Tiger Woods is famous for having worked with many coaches to switch up his tactics and keep exceeding in his performance.
In any other industry, when someone with raw talent — an athlete, a singer, an actor — furthers their career, the first thing they receive is a coach.
Despite a culture that pushes founders to the edge of their physical, mental and personal limits as they build their company, we insist that they fly solo. They’re led to believe that reaching out for support is a sign of weakness.
That stigma is a huge part of the problem. We look up to business magnates, believing that they sailed from a college dorm to the C-suite without breaking a sweat. But we don’t see the vigorous kicking that goes on beneath the surface. As a client of mine once mused, even the best leaders are self-sabotaging themselves at least 30% of the time. I know for a fact that top Silicon Valley billionaires have nutrition, parenting, meditation and life coaches, but they — like half of my own clients — are reluctant to embrace this out in the open.
VCs know that they don’t invest in the business; they invest in the person. Record amounts of money are being funneled into mental wellness startups right now, but investors also need to direct that awareness toward their founders’ well-being. By offering access to a coach to all your portfolio founders, you’ll be tackling the real problems stopping them from pouring their energy into their business, and you’ll without a doubt improve your returns.
1. Business is not always a founder’s main problem
I coach founders and CEOs of startups, and more than half their main life challenges are not work related. They’re getting pulled in multiple directions — some have cancer, others are having an affair, a few are going through IVF, others still are dealing with past grief and traumas.
And when a problem is work related, it’s often a communication or psychological issue: How do I face my fear of failure? How do I lead a team of 50 for the first time? Should I trust my gut?
All this is happening in the midst of Series A raises, hiring and firing employees, acquisitions, and deciding whether to bridge or shut down the business. Imagine how much emotional energy and hours it takes for founders — or anyone, really — to face those intimate issues in isolation while putting on a brave face with investors or at board meetings.
One of the most recurring concerns founders share with me is that they feel alone.
VCs, when you choose to fund someone, you’re also marrying into their past, their family, their personal issues. The full package. Ask yourself — do you currently know the major distractions in the lives of all your portfolio founders? If you don’t, start with the assumption that something is going on in their life other than work and make coaching available to them at any time.
If you commit to helping founders manage their fears, limiting beliefs and blind spots, you’re committing to their potential as a company and industry leader. A healthy leadership is a healthy company.
2. Return on coaching (ROC)
As with elite soccer coaches, the benefits of business coaching are highly visible, without the million-dollar expense. Founders start to make better decisions the first time around. They hire the right talent, rather than hiring, onboarding and firing someone within a month.
They have more honest conversations with stakeholders, avoiding conflict and allowing more people to contribute meaningfully to the business’ growth. They have the proper mindset to fundraise, and their attitude matches the money they’re asking for.
That’s before getting to the physical improvements. My founders have lost weight, stopped smoking and drinking, and have more energy to build a business. If a founder works with chronic fatigue, which many are, it won’t be long before their body cracks. I get calls from clients caught in panic attacks before big meetings, struggling to steady their frayed nerves.
You can fund your founders’ well-being in a variety of ways. In the same way your firm might offer marketing or PR services to portfolio companies, coaching should be part of the package. Firms can make executive coaches available on retainer. You may choose to have a full-time resident coach, available whenever someone needs them.
At the very least, firms should make available a list of recommended coaches. Some coaches specialize in leadership coaching, female founders or health specifically, while others cover various personal and professional skills.
Investors will sometimes offer a handful of free sessions to their founders, but if they want to continue, they are then forced to decide between their personal health and the health of the business — which other people (including your firm) have staked millions of dollars on. It should never be a case of one or the other.
My hope is that in the future, VCs will set aside a percentage of their funds exclusively for mental wellness for founders and executives.
A few VCs have already taken a 1% pledge, but it’s the Europeans who are leading the charge here, with funds from Estonia to Ireland generously covering all founder coaching fees and other support programs. Those I know talk about how 10x growth is possible without burnout.
3. Cut through the stigma to enable founders to make the most of coaching
Founders are resistant to hiring a coach themselves because they’re worried about what their investors and board will think of them. They tell themselves: “If I were normal, and good enough, I wouldn’t need one.”
It’s not just their inner voice talking. When a client of mine joined a Silicon Valley startup, he asked his superiors if coaching could be part of his comp package. They wondered why he needed a coach.
In other industries, connecting someone with a coach is proof of their worth. That’s the conversation investors should be having: You’re good enough for us to give you money, so we’re going to give you someone to accompany you on your journey, so you don’t pretend you can figure it out at every step.
There’s also a negative connotation around the term “mental health” that we should be reframing. Those two words tend to make people think about depression, suicidal thoughts or addiction. Which is mental unhealth. Let’s talk more about mental wellness and founder well-being, which focuses us on the goal we’re working toward.
Eliminating the stigma can start with open conversations about well-being between investors and executives, as well as inviting a coach to talk to your founders about what these sessions entail, and why everyone has something to gain. By shattering the taboo, you’ll enable founders to make the absolute most of that experience, rather than hold back to keep up appearances.
If we start making coaching mainstream today, we might eventually see it as obligatory for all founders.
4. Lead by example
Finally, business leaders and investors need to set an example for the startup community, and especially people at the start of their journeys, that it’s OK to ask for assistance in bettering yourself.
Many VCs, like top CEOs, have coaches. If more simply owned it, they’d have so much power to normalize coaching, and even make #IHaveACoach fashionable. After all, we’re talking about the same industry that made meditation rooms trendy and kombucha an office feature.
Why not make coaching a central topic in future investor conferences, or, as a VC firm, publish a study on how portfolio founders who followed a coaching program saw greater business success?
For example: For years, Union Square Ventures has invested in providing value to their founders and has built a team whose responsibilities include developing leadership training, fostering mentorship circles and connecting founders to coaches. If you let founders see your commitment to human issues, it won’t occur to them that being human is being weak.
These approaches are also important self-promotion for VCs positioning themselves as the next generation of ethical investors. With so many alternative funding options becoming available, founders are seeking VCs who give them more than just capital and who see wellness and diversity and inclusion as inextricable from success.
Founder health and startup health can’t be separated from each other. On some level, all investors know this. So let’s give the people shaping tomorrow’s world the tools to be more comfortable in their own skin and more masterful in leading teams to achieve greatness and incredible returns.
]]>
TechCrunch
TechCrunch
As shocking as it sounds, we could be entering a much better era for small, local businesses.
Modern society produced superstar cities filled with skyscraper office and residential buildings. Now, the populations that once thrived in these urban centers are deciding how to repurpose them for a post-pandemic world.
I caught up with ten top investors who focus on real estate property technology to get a sense of how they’re betting on the future.
They are optimistic overall, because the typically glacial real estate industry now sees proptech as essential to its future. However, they are the most unsure about the office sector, at least as we knew the concept before the pandemic.
They expect remote work to be part of the future in a significant way and foresee ongoing high housing demand in the suburbs and smaller cities. They are especially positive about fintech and SaaS products focused on areas like single-family home sales and rentals. Many are continuing to invest in big cities, but around alternative housing (co-living, accessory dwelling units) and climate-related concepts.
Most surprisingly, some investors are actually excited about physical retail. I examined the latest evidence and found myself agreeing. As shocking as it sounds, we could be entering a much better era for small, local businesses. Details farther down.
(And before we dig in below, please note that Extra Crunch subscribers can separately read the people cited below responding fully in their own words, with lots of great information I wasn’t able to explore. One other thing, we did suggest they mention their own investments to illustrate what they believe about the sector. )
When the office is more of a luxury
The pandemic combined with existing trends has made office renters “more akin to a consumer of a luxury product,” explains Clelia Warburg Peters, a venture partner at Bain Capital Ventures and long-time proptech investor and real estate operator.
Landlords who have “largely been in a position of power since the 1950s” now have to put the customer first, she says. The “best landlords will recognize that they are going to be under pressure to shift from simply providing a physical space, to helping provide tenants with a multichannel work experience.”
This includes tangible additional services like software and hardware for managing employees as they travel between various office locations. But the market today also dictates a new attitude. “These assets will need to be provided in the context of a much more human relationship, focusing on serving the needs of tenants,” she says. “As lease terms inevitably shorten, tenants will need to be courted and supported in a much more active way than they have been in the past.”
The changes in office space may be more favorable to the supply side in suburban areas.
“Companies are going to have to offer employees space in an urban headquarters,” Zach Aarons of MetaProp tells me (his firm just published a very positive report on the sector). But many will also want to offer ”some sort of office alternative in the suburbs so the worker can leave home sometimes but not have to take a one-hour train ride to get to the office when needed.”
“If we were still purchasing hard real estate assets like many of us on the MetaProp team used to do in previous careers,” he added, “we would be looking aggressively to purchase suburban office inventory.”
Most people thought that remote work was here for good and would impact the nature of office space in the future.
Adam Demuyakor, co-founder and managing director of Wilshire Lane Partners, is generally bullish on big cities, but he notes that startups themselves are already untethering from specific places. This is a key leading indicator, in TechCrunch’s opinion.
“Something that has been interesting to watch over the past year is how startups themselves have begun to evolve due to newfound geographic flexibility from the pandemic,” he observes. “Previously, startups (especially real-estate-related startups) felt pressure to be ‘headquartered’ near where their customers, prospective capital sources and pools of talent were located. However, we’ve seen this change over the past few months.”
In fact, a recent report by my former colleague Kim-Mai Cutler, now a partner at Initialized Capital, highlights these trends in a regular survey of its portfolio companies. When the pandemic began, the Bay Area was still the number one place that founders said they’d start a company. Today, remote-first is in first place. Meanwhile, the portfolio companies are either going toward remote-first or a hub-and-spoke model of a smaller headquarters and more far-flung offices. Those who maintain some sort of office say they will require significantly less than five days a week. Nearly two-thirds of respondents said they would also not adjust salaries based on location!
That’s a small sample but as Demuyakor says, “Startups (a) are frequently the most adept at utilizing the types of technology necessary for effective remote work and (b) simultaneously have to compete ferociously for talent. As such, I think we may be able to infer what the ‘future of work’ may look like as we observe what startups choose to do as the pandemic passes.”
Some landlords (with big loans) and large cities (with big budgets) are making a push to repopulate their offices quickly, and some large companies are loading up on office space or reaffirming their commitments to current locations.
Maybe efforts like these, plus the natural desire to network live, will bring back the industry clusters and pull everyone back to the old geographies? Maybe something close to 100% of what we saw before? What does that look like?
In such a scenario, some pandemic-era changes will persist, says Christopher Yip, a partner and managing director at RET Ventures. “A populace that has become sensitized to public health considerations may well gravitate toward solo forms of transportation (cars and bicycles) instead of mass transit, and parking-related and bike-sharing tech tools may likely thrive. From a real estate management perspective, technology that makes high-density living more comfortable and healthier will also increase, as consumers will become increasingly attracted to touchless technology and tools that facilitate self-leasing.”
Here’s the other scenario that he lays out “if a large number of jobs remain fully remote.”
“In theory, retail and office properties could structurally continue to suffer, and there has been some talk from government officials in certain regions about converting office properties into affordable housing,” he details. “If market-rate vacancies in cities remain high, there will be increasing demand for short-term rental platforms like Airbnb and Kasa, which enable landlords to gain revenue from hotel-type stays even in a market where residential demand is not strong.”
Vik Chawla, a partner at Fifth Wall, sketches out a middle-of-the-road scenario. “We believe that major cities will continue to attract knowledge workers and top talent post-pandemic,” he says, “though we expect remote work to become an increasingly critical component to the work economy, meaning that there will be increased flexibility in terms of time spent in the office versus elsewhere.”
This would still mean some sort of long-term price decline. “At a city level, this means that rents should taper relative to pre-pandemic levels due to lesser demand,” he believes. “That said, the real estate ecosystems in cities that have experienced growth throughout the pandemic will enter a period of innovation, and with it, see an increase in housing density, ADUs and modular building techniques.”
Andrew Ackerman, managing director of UrbanTech for DreamIt Ventures, also sees a gentle deflation of commercial office prices over time, followed by some complex space-management questions.
“[T]he return to work will likely result in more flexible work arrangements rather than the demise of the office which, as leases renew over the next 5-10 years, will lead to a gradual meaningful-but-not-catastrophic reduction in the demand for office space. The question is, what then happens to the excess office space?”
“Office to residential conversion is tricky,” he elaborates. “Layout is a major constraint. Many modern offices have deep, windowless interior space that is hard to repurpose. But even with narrow layouts, the structural elements are often in the wrong place. Drilling thousands of holes in structural concrete so you can move plumbing and gas to the right places is a heavy lift.”
This might just lead to new types of still-valuable uses? “One of the areas that I’m still investigating is whether co-living or microunits might be a more attractive conversion option. Turning an office break room and interior bullpens into a shared kitchen, dining area, and recreation or work flexspace may be a better way to repurpose deep interior space without a very costly retrofit. And if you don’t have to reroute too much plumbing, it may even be possible to convert (and convert back!) individual floors as market demand for office and residential space fluctuates over time.”
All respondents saw proptech being a core part of the next era of big cities (of course), however bullish or bearish they may be about the office itself.
A new equilibrium for residential
Housing availability has become even more limited in most places during the pandemic, with many more people looking to buy and fewer people wanting to sell. This is even though the previously hottest cities have seen major rental price drops.
Demuyakor of Wilshire Lane is staying focused on the housing problem, and solutions to it like co-living. “Despite the pandemic, it is still difficult for millennials and Gen Z to afford to live in the most expensive cities (New York, San Francisco, Los Angeles, etc.) at current wage levels,” he says. “As such, we believe that we will continue to see demand for products and solutions that can continue to help alleviate costs and burdens of living in major cities. For example, we think that at its core, co-living is an economic decision. Solutions that continue to help people live where they want to live more easily (ADUs are another example of this) will continue to thrive.”
Casey Berman, managing director and general partner of Camber Creek, thinks that “cities will continue to attract people to live, work and play because they offer density and opportunities for experiences that people crave even more now. To the extent all of this is true, there will be renewed demand for urban spaces and properties to take advantage of that demand.”
He says that the firm has been investing in products to make dense living safer and more convenient and “we expect those solutions will become increasingly popular. Flex allows tenants to pay rent online in easier-to-manage installments and in the process makes it more likely that landlords will receive payment on time. Latch’s access control devices are in one out of 10 new multifamily buildings. A lot of people purchased a pet over the past year. PetScreening makes it easy to manage pet records and confirm when a pet is a service or support animal.”
Robin Godenrath and Julian Roeoes, partners at Picus Capital, generally share this viewpoint and describe how new living arrangements in cities could allow for more radical changes to how people live.
“Flexible living solutions will allow remote workers to spend time across different cities with a fully managed, affordable and safe rental option for short-to-long-term urban living,” he says, “while commercial conversion to residential will play a key role in driving down per square foot prices enabling long-term returning residents to afford less densified space. Although co-living densifies multifamily buildings, we believe it will remain an interesting sector as the continued shift to remote work will make living communities increasingly important considering the reduced social interaction on the job.”
But modern proptech is also making the suburbs and beyond more appealing in the long run, according to many. Great new technologies for living can exist anywhere you are.
Proptech has also helped fuel the new suburban boom. “There is an ongoing trend of reverse urban migration causing an uptick in the demand for suburban-style living,” he says. “Proptech companies have played a significant role in enabling this shift, specifically via digitizing the home buying, selling and renting transaction processes (e.g., iBuyers, alternative financing models and tech-enabled brokerages). Additionally, proptech companies have played a key role in reducing physical interactions through remote appraisals, 3D/VR viewings and digital communications thus enabling homebuyers and sellers to efficiently and safely transact throughout the pandemic.”
Ultimately, the same technologies that could make cities more affordable will also help out in the suburbs. “We strongly believe that the acceleration of the digitalization of the home transaction process coupled with the significant increase in demand for suburban-style housing and evolving buyer profiles (e.g., tech-savvy millennials) opens up a multitude of opportunities for proptech to significantly impact suburban living across construction, access and lifestyle. This includes companies focusing on built-to-rent developments, modular homebuilding, affordable housing, community building and digital amenities.
Many investors who we talked to highlighted the single-family rental market trend. Here’s Christopher Yip again from RET.
“One of the unheralded trends of the past decade has been the rise of the single-family rental (SFR) market,” he says “with a significant number of major investors moving into this asset class. The SFR space is poised to benefit from the migration from cities, and the tech that supports SFR will likely have positive ripple effects across the industry.”
“SFR portfolios are particularly challenging to operate efficiently and at scale; compared with a multifamily property, they have more distinct unit layouts and are more spread out geographically,” he explains. “Technology has the ability to streamline operations and maintenance for SFR operators, with smart home tools like SmartRent facilitating self-touring and management of these distributed portfolios. We’re bullish on this space and are keeping a close eye on proptech tools that serve this market.”
Andrew Ackerman of DreamIt agrees. “Single-family has been neglected, slowly growing more interesting both from an asset and proptech perspective for some time. For example, we invested in startups like NestEgg and Abode who service this ecosystem … prior to the pandemic. COVID has been good to these startups and brought more attention to the opportunities in single-family in general.”
Stonly Baptiste and Shaun Abrahamson, co-founders of Urban.us, already see a world of options unfolding across geographies, with choices like co-living and short-term rentals letting people find new lifestyles. “Portfolio companies like Starcity are really thriving as co-living doesn’t just solve for cost, but also for a key overlooked issue — access to community. We also see room for more nomadic lifestyles. A lot of the discussion about Miami is about people moving there, but it seems like a more interesting question for a lot of places is maybe whether or not people will spend a few months of the year there. So for remote workers this might mean places near specific activities like mountain biking, surfing, snowboarding etc. Starcity makes it easy to move between city locations and Kibbo takes this far beyond the city by building communities around van life.”
Here’s how all these changes are adding up for the suburban market, as mapped out by Clelia Warburg Peters of BCV.
“The residential transaction disruption is now settling in three core categories: iBuyers (who buy homes directly from sellers and ultimately hope to own the sell-side marketplace), neobrokers (who generally employ their agents and use secondary services such as title mortgage and insurance to increase their revenue) and elite agent tools (platforms or tools focused on the top agents).”
This combination of innovations are changing residential real estate as we know it. “[C]onsumers are increasingly open to alternative financing tools, including home-equity-based financing models (where you sell a stake in your home, or you buy into full ownership in a home over time). The growth and proliferation of these new models are consolidating the whole residential market so that brokerage sales commissions and commission from the sale of mortgage, title and home insurance are now functionally one large and intertwined disruptable market.”
The surprising revival of neighborhood retail
Humans seem to love the concept of a traditional Main Street full of bustling, walkable local businesses. But the hits have kept coming to the people trying to successfully operate independent retail storefronts.
E-commerce began cutting into traditionally thin margins with the rise of Amazon and the 90s wave of “e-tailers.” More recently, art galleries, high-end restaurants and boutiques became a harbinger of gentrification in many cities. Many commercial retail landlords in these locations aggressively priced rents as more residents moved in who could afford higher prices, ultimately contributing to gluts of empty storefronts in prime locations.
The pandemic seemed to be the final blow, with even the most loyal shoppers turning to order online while local businesses stayed closed.
And yet, a range of investors are strangely optimistic. Even though the pandemic upended social and economic activity for more than a year, most agreed that IRL retail experiences are an essential aspect of modern life.
“Humans are fundamentally social animals and I think we will all be hungry for in-person experiences once it is safe to return to them. Additionally, I think the shift away from working five days a week in the office is going to create a greater desire for ‘third spaces’ — not home, not a formal office environment,” said Peters.
“I do think we will continue to see more ‘Apple store’-type retail experiences, where the focus is less on selling inventory and more on creating an environment for customers to physically interact with goods and experience the brand ethos beyond a website. Because I anticipate that retail rents are going to be meaningfully lower at the end of the pandemic, I actually think we will see even more experimentation than we did pre-COVID. It will be a very interesting period for retail.”
Many others held views in this direction, whether they are investing specifically in retail-related tech or more generally in third-space ideas.
“It’s true that retail has been in flux for more than a decade; the list of common e-commerce purchases has expanded from books and clothing to prepared meals and groceries. It’s also true that the pandemic has accelerated e-commerce’s growth, to the detriment of brick-and-mortar retail,” says RET’s Yip. “But people are still human and crave in-person experiences. Even if cities never bounce back fully, major metropolises will still have enough foot traffic to support a fair amount of retail, and innovative models like pop-up shops can be brought in to help address vacancies. It should also be noted that the public markets still have some confidence in the retail space. While the major REITs struggled in early to mid-2020, many have recovered substantially, and several have actually surpassed their pre-pandemic figures. It has been a bad decade for retail — and a very bad year — but it is just too soon to close the book on the sector.”
Godenrath and Roeoes of Picus say movie theaters are just one example of a retail sector poised for success when public life resumes at scale post-pandemic.
“Cinemas, many of which are key shopping center anchor tenants, were already reinventing the traditional theater experience by offering a more holistic experiential solution (e.g., reserved seating, 4DX visuals, in-theater restaurants, cafes and bars) and the pandemic has led to an expansion of these offerings (i.e., private theater rentals and events). We have the opinion that this trend will continue to expand across the entire retail real estate industry from restaurants (immersive culinary experiences) to traditional retail (integrated online and offline shopping experiences) and believe that proptech will play a defining role in helping retail real estate owners identify potential tenants and market properties as well as in helping retailers drive in-store customer engagement and gain key insights into the customer journey.”
The internet is also a friend these days, surprisingly! “We also see a lot of potential for hybrid models combining online and offline experiences without friction,” they say. “Taking the fitness sectors as an example we can imagine a new normal where in-studio courses are broadcasted to allow a broader participant group and apps tracking fitness and health progress throughout in-studio visits and at-home workouts.”
I have a few additional reasons to believe in the future of retail that I didn’t hear from any of the investors I interviewed.
You can also see how retail intersects with many other solutions investors are betting on, particularly to improve the appeal of cities and solve for macro problems like climate change.
“Cities have some massively underutilized assets, perhaps the biggest being public spaces that are allocated to cars,” Baptiste and Abrahamson say. “So one change we think will become permanent is reallocating parking spaces away from private vehicles to micromobility (bike/scooter/board lanes, parking, etc.). We’re seeing a lot of demand for portfolio companies like Coord (manages curb space starting with commercial vehicles and smart zones), Qucit (manages bike and scooter share operations in many large cities) and Oonee (secure bike/scooter/board parking).”
That’s just the start of the virtuous cycle they foresee.
“As [car removal] happens, the use cases like logistics can shift to electric micro-EVs. Similarly, parklets or seating areas increase social spaces. The EU is setting the pace for banning cars, but overall reduced access to streets for cars is going to be a big change. And likely will make cities attractive — yes, you give up private living space, but you’re going to get a lot more common/social space. This is also likely to drive more co-living so you can decrease the cost basis for being in a city, but get a lot more from shared spaces, which have no real comparison in lower density communities.”
Demuyakor of Wilshire Lane is betting in the same direction.
“One of the key tenets of our overall strategy has always been a focus on space utilization and identifying the best ways technology can monetize underutilized spaces. This can be seen clearly with many of our newest investments: Stuf and Neighbor (monetization of basements, parking garages and other vacant spaces), MealCo (monetization of vacant kitchens), WorkChew (monetization of restaurant seating areas, hotel lobbies and conference rooms), and Saltbox (monetization of empty warehouses). We believe that landlords can certainly use these types of strategies to help mitigate increased levels of vacancies that we’re seeing across the real estate industry today in the medium term.”
If this thesis pans out, retail may become more about shared spaces. “With WorkChew in particular, which just announced funding this week, we’re seeing a ton of demand for their product both on the demand side and the supply side. Hotels and restaurants are excited to partner with them to monetize their less-utilized spaces and infrastructure,” said Demuyakor. “And of course, employers and companies love [it] as an easy amenity that can be offered to their hybrid workforces that increasingly want to spend more time out of the HQ office.”
I have a few additional reasons to believe in the future of retail that I didn’t hear explicitly from the investors I interviewed.
- First, millions of new businesses have been created during the pandemic, to the surprise of even economists and policymakers. A large portion appear to have a very local angle, whether food delivery (cupcakes) or services (on-site haircuts) or internet-first products with strong local followings (much of Etsy). These entrepreneurs went internet-first and now, as commercial rents plummet, they have sufficient revenue to support a physical presence.
- Second, most local business that have sustained themselves during the COVID-19 era figured out how to succeed on the internet. To see which ones in your vicinity are weathering the storm, just open one of your preferred on-demand delivery and services apps and place an order.
- Third, as noted by respondents and available data, landlords are already starting to drop prices, creating a renter’s market for the first time in decades.
- Fourth, there are whole new types of financing opening up to more traditional businesses that could enable any company with a successful online side hustle, hobby (or perhaps larger project) to get funding for expansion. (This reason is perhaps the most speculative, but we are trying to figure out the future here at TechCrunch.) For example, Shopify has just invested in Pipe.com, a new “platform for trading recurring revenue.” Although the companies are not saying much now about the relationship, it’s possible to imagine a bunch of successful small(ish) businesses on Shopify suddenly getting a new kind of capital infusion right as the math is suddenly much better for a storefront location.
If you roll all of this up with other broader shifts in how we think about cities, like making them more climate-friendly through allowing density and bike lanes, you can start to see a world emerging that sounds a lot more like the fantasies of a New Urbanist than the world before the pandemic.
At the same time, these concepts are being deployed across smaller cities, suburbs and towns: All will compete to offer the highest quality of living — unless the old network effects of industry clusters return miraculously.
And let’s say the industry clusters don’t cluster like they used to. It’s possible that many landlords, lenders and city budgets will have to retrench soon, creating a drag on the economies of otherwise-attractive cities.
Even in this case, you can imagine a rebirth for places like New York and San Francisco focused around housing, retail and amenities. Maybe one day, we’ll look back at recent decades as the bad old days before we collectively bottomed out during the pandemic and had to decide on the right answers for the long-term.
And with that, I invite readers to go check out the full sets of responses from the investors I interviewed. Each person offered a lot more than I was able to fit into this already-too-long article and is worth reading in detail. Extra Crunch subscription required, so you can support our ongoing coverage of these changes.
I’ll be covering the future of proptech and cities more soon. Have other thoughts about all of this? Email me at eldon@techcrunch.com.
]]>
TechCrunch
TechCrunch
India is the second-largest demographic represented in the new batch. The world’s second-largest internet market has delivered 43 startups in the new batch, another record figure in the history of the storied venture firm. (For comparison, the W20 batch had 25 Indian startups, up from 14 in S20, 12 each in S19 and W19 and one each in W16, S15 and W15.)
“YC going remote has helped make YC more attractive to companies at different stages and far away geographies. For companies in India, founders no longer have to spend three months away from their customers or teams. Covid has also taught us that building a program that is remote and more software based makes YC more accessible to founders around the globe,” the firm said in a statement to TechCrunch.
“When it comes to choosing founders in India, we accept them based on the same criteria we judge companies from anywhere else. Founders must be able to communicate their local context to investors. That is an important skill.”
Here’s a list of startups, in no particular order, from India that have made it to YC W21, with some context — wherever possible — on what they are attempting to build (several have elected to stay off the record).
QuestBook, from CreatorOS, is an app for professionals to teach in bite-sized courses using chat and a mobile-first experience. We wrote about CreatorOS last year.
Leap Club is attempting to build a Good Eggs for India. Leap Club users can order fresh and organic groceries sourced from local farms through the startup’s website or through WhatsApp. The startup says it delivers the item to customers within 12 hours of harvesting. Leap Club is already garnering over $14,000 in monthly revenue.
CashBook is building a cash account app for small businesses in India. There are over 60 million small businesses in the country, nearly all of which currently rely on traditional ways — pen and paper — for bookkeeping. The startup launched its app just six months ago and has already amassed 200,000 monthly active users. In the month of February, CashBook logged cash transactions of $511 million.
GimBooks is attempting to solve a similar problem as CashBook, though from a different angle. The startup says it offers industry-based invoicing and bookkeeping with integrated banking and payments. Its app has been downloaded more than 1.4 million times, amassed over 11,000 paying customers and clocked revenues of over $450,000.
BusinessOnBot is banking on the popularity of WhatsApp in India, where the Facebook-owned app has amassed over 450 million monthly active users. BusinessOnBot says it is building Shopify on WhatsApp for direct-to-consumer brands and small and medium-sized businesses, helping them acquire users and automate sales.
ZOKO is helping businesses do sales, marketing and customer support on WhatsApp.
Prescribe is a Shopify for hospitals. Its platform is aimed at helping doctor’s offices run their business online. Users can book appointments, chat with the doctor, pay and refer friends on WhatsApp.
Chatwoot is an open-source customer engagement suite alternative to Intercom and Zendesk. Over 1,000 companies are already using Chatwoot and it’s clocking $32,000 in ARR from six customers.
Weekday is helping companies hire engineers who are crowdsourced by their network of scouts. The startup says it has found a way to solve the biggest problem with referrals — that it doesn’t scale.
Fountain9 helps food brands and retailers reduce food wastage. According to some estimates, over $260 billion worth of food is wasted every year due to mismanaged inventory.
Dyte is attempting to build a Stripe for live video calls. The startup says a firm can integrate its branded, configurable and programmable video calling service within 10 minutes using the Dyte SDK.
YourQuote has built a writing platform, with over 100 million posts. It has over 250,000 daily active users. The startup clocked revenues of $200,000 last year and is profitable.
Fifthtry is building a GitHub for product documentation. The tool blocks code changes until documentation has been approved. It has piloted its tool with three companies, all of which have over 100 developers. The startup plans to launch its tool publicly next month.
Voosh is building an OYO for restaurants and dark kitchens in India, helping them improve their economics using tech.
Kodo is building a Brex for India, helping Indian startups and small businesses secure corporate credit cards. (Banks and other credit card companies are still not addressing this opportunity. The problem Brex solved in the U.S. is even acute in India, Deepti Sanghi, co-founder and chief executive of Kodo, said in the presentation.
Krab provides instant loans for trucking companies in India. India’s logistics market, despite being valued at $160 billion, remains one of the most inefficient sectors that continues to drag the economy. In recent years, a handful of startups have started to explore ways to work with trucking companies.
Bueno Finance says it wants to help the next billion users in India get access to financial services. It says it wants to solve for short-term cash needs of customers by using digital credit card over UPI. It was to build a Chime for India, and has amassed 70,000 customers.
Betterhalf is building a Match.com for 100 million Indians. It says it is generating $75,000 in monthly revenues, a figure that is growing 30% every month.
Pensil is helping teachers who use YouTube monetize their courses. “YouTube is the largest education platform in India — but it’s not built for teachers,” said Surender Singh, co-founder of Pensil, at the presentation on Tuesday. The startup has built tools to allow teachers to create content, facilitate discussions and collect payments.
AcadPal operates an eponymous app for India’s 10 million teachers to share homework with a tap. The startup is attempting to target a $1.4 billion market, which consists of over 400,000 private schools.
Pragmatic Leaders is attempting to build a platform to provide cost-effective alternative to an MBA. It is already clocking a monthly revenue of $112,000 and is cash-flow positive.
Splitsub is addressing a problem that tens of millions of users in India face — subscription fatigue. It says it has built a Pinduoduo for online subscriptions in India, allowing group buying and sharing of online subscriptions for services such as Netflix and Spotify.
Zingbus has built a platform for bus travel between Indian cities. (Several startups in India are helping users get cabs, three-wheelers autos and two-wheelers bikes. Buses have remained largely untapped.)
Tilt is building a docked bike-sharing platform for Indian campuses. The startup, which has generated about $20,000 in revenues this month so far, says it has been profitable for the past 18 months.
FanPlay is a platform for social media influencers, helping them monetize by playing mobile games with their fans and followers.
(Also read: Why Y Combinator Went 8,725 Miles Away From Mountain View To Find The Next Big Startup)
In India only a fraction of the nation’s 1.3 billion people currently have access to insurance and some analysts say that digital firms could prove crucial in bringing these services to the masses. According to rating agency ICRA, insurance products had reached less than 3% of the population as of 2017.
An average Indian makes about $2,100 a year, according to the World Bank. ICRA estimated that of those Indians who had purchased an insurance product, they were spending less than $50 on it in 2017.
Three startups in the current batch are planning to disrupt this market, which is largely commanded by state and bank-backed insurers.
GroMo is an app for independent agents to sell insurance in India. Most insurance policies in India are sold by agents. The startup says it is already generating monthly revenues of over $200,000.
Bimaplan is attempting to replace the agents with an app and reach users by a referral network. The app launched last month and has already sold 700 policies this month.
BimaPe helps users better understand their policies, and make informed decisions about whether those policies are right for them. The startup, leveraging New Delhi’s new regulations, is using a government issued ID card to fetch insurance policies.
Codingal is an online, after-school program for K-12 students in India to learn computer science. There are roughly 270 million K-12 students in the country.
Unschool provides professional education for college students in India. The founders say, “As former leaders in youth-run organisations with 3,000 members and edtech startups in India, we saw how colleges are not preparing students for the real world.”
Flux Auto builds self-driving kits for trucks.
SigNoz is an open-source alternative to DataDog, a $30 billion company, helping developers find and solve issues in their software deployed on cloud. The startup says recent laws such as GDPR and CPRA have helped drive adoption of SigNoz.
Pibit.ai are APIs to turn unstructured documents into structured data.
Invoid creates identity workflows in India. It’s tapping into a huge market opportunity: About 11 billion know-your-customers authentication is conduced by firms in India each year.
Redcliffe Lifesciences performs genetic testing and IVF treatments across India. Its revenue in March has topped $600,000.
Veera Health is an online clinic that treats Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), a lifelong condition that affects 10-20% women in India. The startup says it launched 12 weeks ago, and 85% members have reported feeling “in control” of their PCOS after 1 month.
Snazzy is SmileDirectClub for India. The startup says it sells clear aligners that are 70% cheaper than those sold by dentists.
BeWell Digital is building the operating system for India’s 1.5 million hospitals, labs, clinics and pharmacies by starting with insurance regulatory compliance.
Triomics is operating a SaaS platform for end-to-end automation of clinical trials.
]]>
TechCrunch
TechCrunch
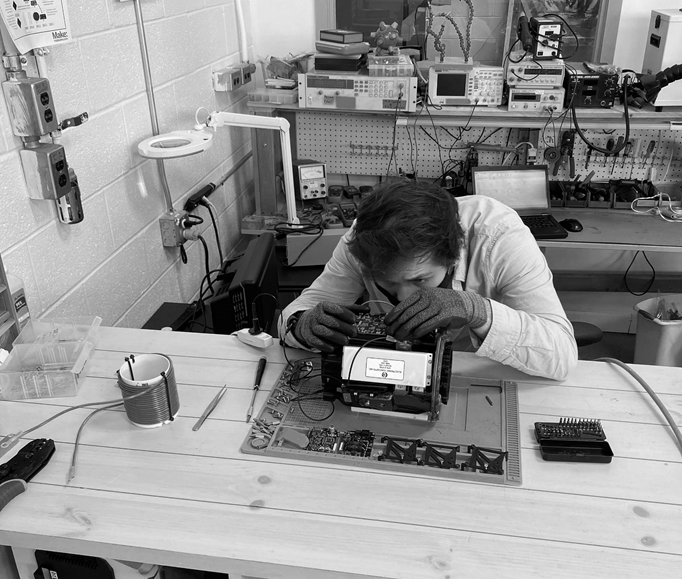
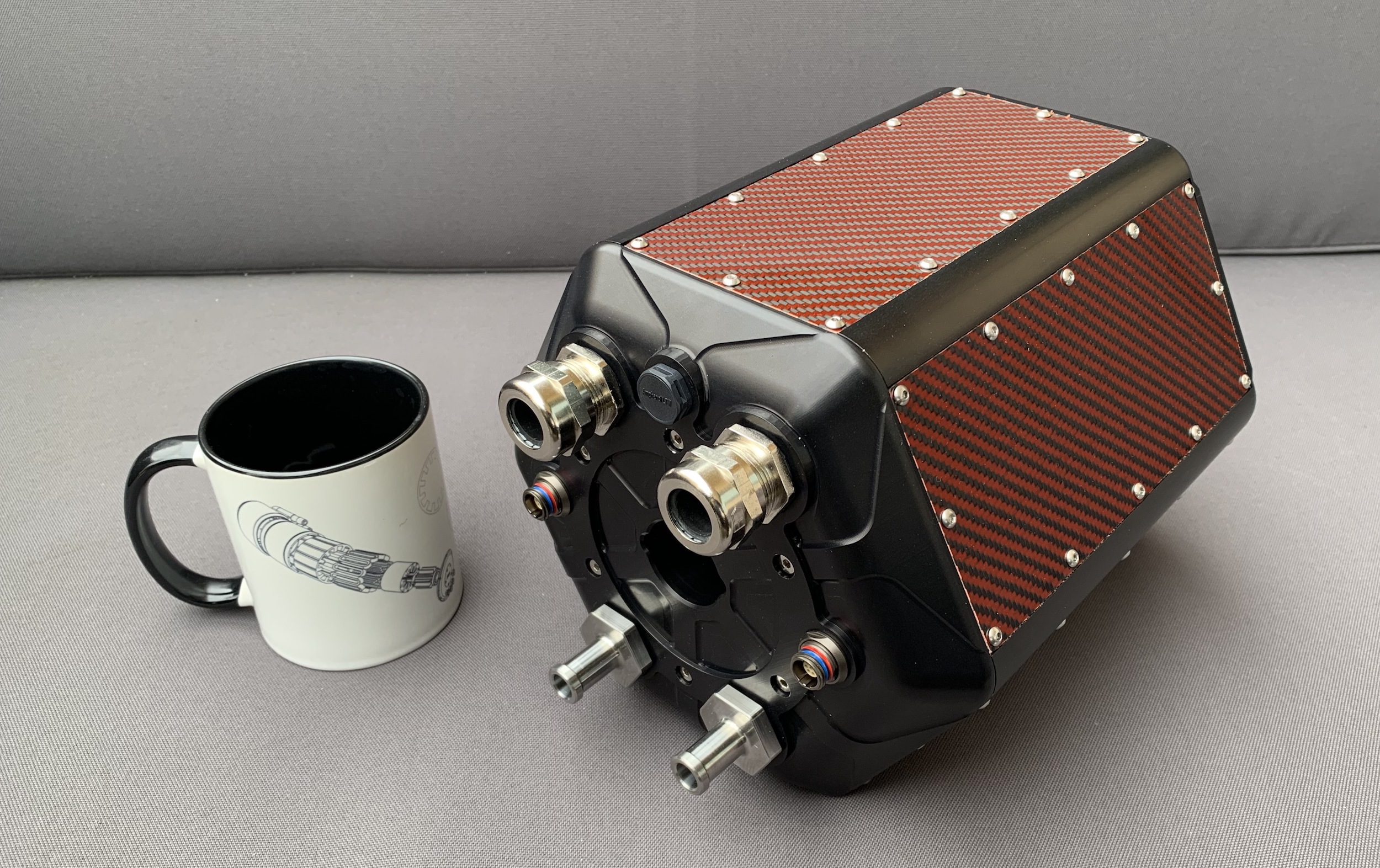
The small founding team — CEO Jason Sylvestre, CTO Max Liben, and COO Eric Maciolek — met in college while participating in an electric vehicle building and racing program. After stints in the tech and automobile industry (including at Tesla), the crew came back together when they saw that the Department of Energy was offering a bounty for improved high power density electric motors.
“The problem was uniquely suited to our abilities, and passions too — we’re excited about this stuff. We care about decarbonization of the different transit sectors, and aviation is going to become a growing part of the global carbon footprint over the next few decades as electric improves ground vehicles,” said Liben. “We just kinda decided to take a leap of faith, and applied to Y Combinator.”
Electric flight isn’t so much a wild idea as one that’s in its early, awkward stages. Lightweight craft like drones can do a great deal with the batteries and motors that are available, and converted small aircraft like seaplanes are able to make short flights, but that’s about the limit with the way things are today.
The problem is primarily a simple lack of power: The energy required to propel an aircraft fast enough to generate lift grows exponentially as the size and mass of the plane increase. A handful of kilowatt-hours will serve for a drone, and a few EV-scale batteries will work for a light aircraft, but beyond that the energy required to take flight requires batteries the bulk and weight of which make flight impractical.
Of course, it doesn’t have to be like that. And there are two general avenues for improvement: better batteries or better motors. So either you can fit more energy in the same mass or use what energy you have more efficiently. Both are being pursued by many companies, but H3X claims to have made a huge leap forward in power density that could unlock new industries overnight. While even an improvement of 10% or 20% in power per kilogram (e.g., a 50-pound motor putting out 120 horsepower rather than 100) would be notable, H3X says its motor is performing at around 300% of the competition’s output.
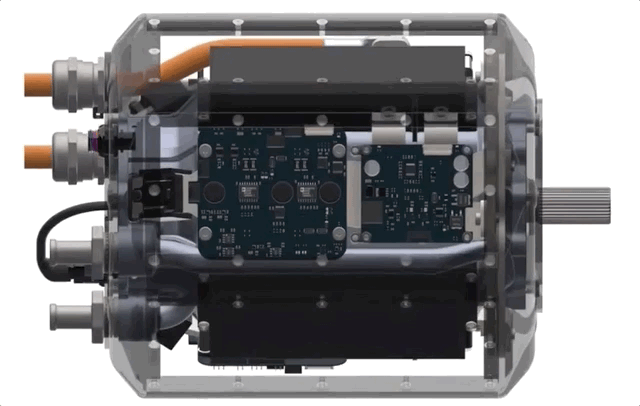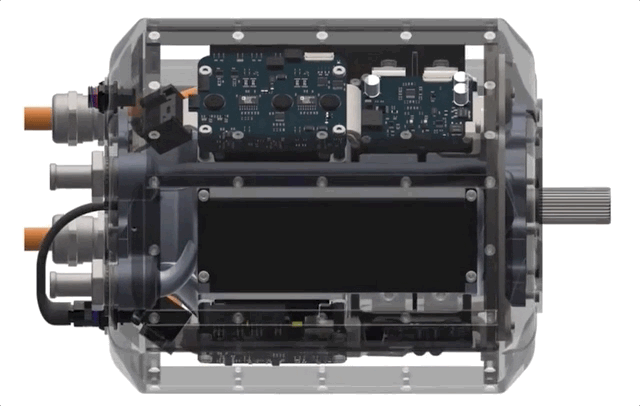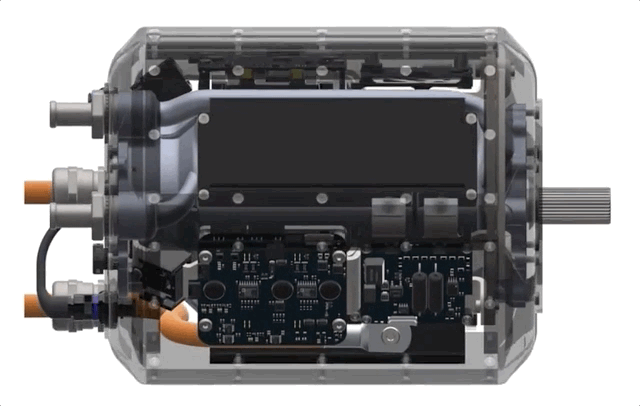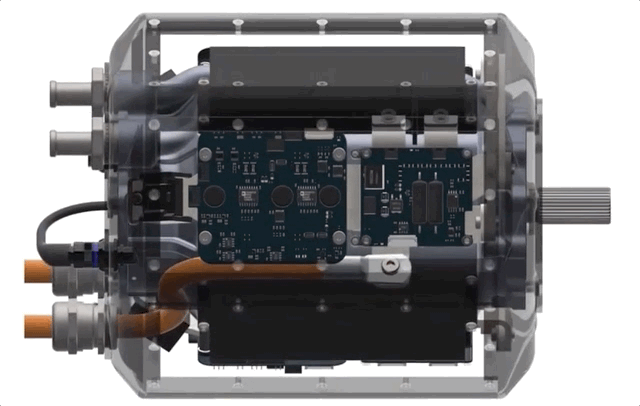
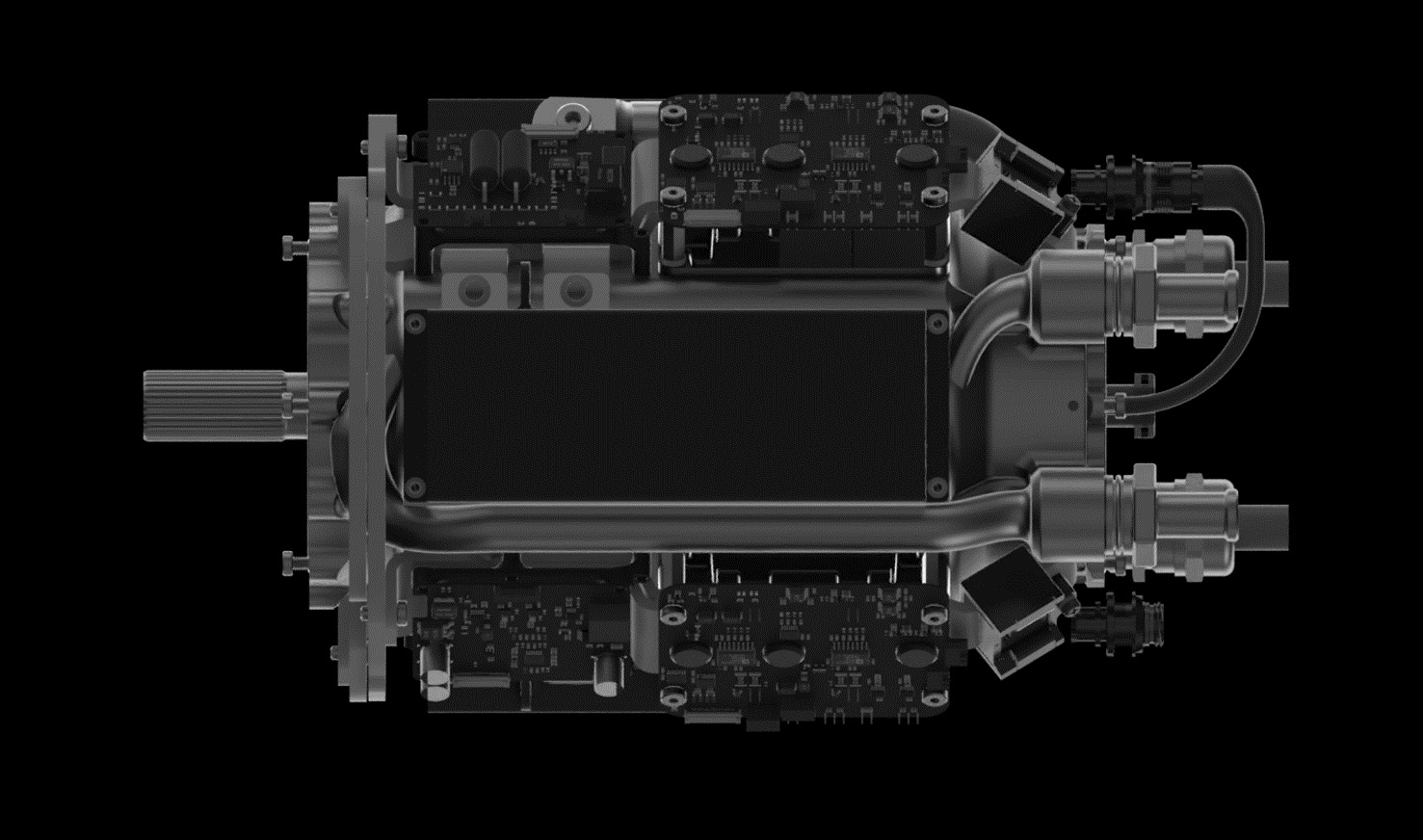
How? It’s all about integration, Liben explained. While the pieces are similar in some ways to motors and power assemblies out there now, the team basically started from scratch with the idea of maximizing efficiency and minimizing size.
Electric motors generally have three main sections: the motor itself, a power delivery system and a gearbox, each of which may have its own housing and be sold and mounted separately from one another. One reason why these aren’t all one big machine is temperature: The parts and coolant systems of the gearbox, for instance, might not be able to operate at the temperatures generated by the motor or the power system, or vice versa. Put them together and one may cause the other to seize up or otherwise fail. The different sections just have different requirements, which seems natural.
H3X challenges this paradigm with a novel integrated design, but Liben was careful to clarify what that means.
“We’re not just taking the inverter box and slapping it on top and calling it integrated,” he said. “All the components are all intimately connected to the same housing and motor. We’re making a truly integrated design that’s one of the first of its kind at this power level.”
And by “one of the first” he doesn’t mean that Airbus has one in some powertrains, but rather that there have been research projects along these lines — nothing intended for production.
The idea that no one else has gone this far in putting everything in the same box at scales that could be used commercially may sound suspicious to some. One would think that the existing players in aerospace would have been barking up this tree for years, but Liben said large companies are too slow to innovate and too invested in other methods, while smaller ones tend to avoid risk by improving incrementally on successful existing designs and competing among themselves. “No one is targeting the level of performance we’re looking at right now,” he said.
But it isn’t like H3X stumbled over a single advance that magically tripled the performance of electric motors.
“We’re not relying on one big tech or something — there’s no magic bullet,” Liben said. “There are a few improvements that have very significant gains, like 50% better than the state of the art, and lots of areas that add 10%-20%. It’s good from the technical risk side.”
He went into considerable detail on a lot of those improvements, but the less technical-minded among our readers, if they’ve even read this far, might close the tab if I tried to recount the whole conversation. To be brief, it amounts to combining advances in materials, manufacturing and electric components so that they act synergistically, each enabling the other to be used to best effect.
For instance, recently improved power switching hardware can be run at hotter temperatures and handle higher loads — this raises performance but also allows for shared cooling infrastructure. The shared infrastructure can itself be improved by using new pure-copper 3D-printing techniques, which allow more cooling to fit inside the housing. Using 3D printing means custom internal geometries so that the motor, gearbox and power delivery can all be mounted in optimal positions to one another instead of bolted on where existing methods allow.
The result is an all-in-one motor, the HPDM-250, that’s smaller than a lot of the competition, yet produces far more power. The best production motors out there are around 3-4 kilowatts per kilogram of continuous power. H3X’s prototype produces 13 — coincidentally, just above the theoretical power density that would enable midrange passenger aircraft.
There is the risk that stacking cutting-edge techniques like this makes the cost rise faster than the performance. Liben said that while it’s definitely more expensive in some ways, the smaller size and integrated design also lead to new savings in cost, time or material.
“People think, ‘3D-printing copper, that’s expensive!’ But when you compare it to the super high-performance windings you’d need otherwise, and the different ways that you manufacture them, that can require a lot of manual steps and people involved … it can be a lot simpler printing something,” he explained. “It can be counterintuitive, but at least from my BOM [bill of materials] cost, when you’re selling something three times smaller than the other guy, even if it’s high-performance materials, it’s actually not as expensive as you’d think. Based on the customers we’ve talked to so far, we think we’re in a good spot.”
Servicing a fully integrated motor is also fundamentally more complex than doing so for an off-the-shelf one, but Liben noted that they were careful to think about maintenance from the start — and also that, while it may be a little harder to service their motor than an ordinary electric one, it’s much, much simpler than servicing even the most reliable and well-known gas-powered motors.
Despite the huge gains H3X claims, the target market of passenger aircraft is hardly one that they, or anyone, can just jump into. Heavily regulated industries like air travel require years of work and technology proving to change a fastener style, let alone the method of propulsion.
So H3X is focusing on the numerous smaller, less regulated industries that could use vastly improved electric propulsion. Cargo drones, electric boats and air taxis might still be rare sights on this planet, but a big bump to motor power and efficiency might be what helps tip them from niche (or vaporware) to mainstream. Certainly all three of those applications could benefit hugely from improved range or payload capacity.
Graduating to passenger flights isn’t a distant dream, exactly, suggested Liben: “We’re already on our way — this isn’t 20-years-out type stuff. In the last few years the timelines have shrunk drastically. You could have a full-battery electric vehicle soon, but it isn’t going to cut it for longer flights.”
There’s still a role for motors like H3X’s in hybrid aircraft that use jet fuel, batteries and perhaps even hydrogen fuel cells interchangeably. Like the switch to electric cars, it doesn’t happen all at once and it doesn’t need to for the purposes of their business. “That’s the great thing about motors,” Liben said. “They’re so ubiquitous.”
H3X declined to disclose any funding or partners, although it’s hard to believe that the team could have gotten as far as it has without some kind of significant capital and facilities — this sort of project outgrows the garage workbench pretty fast. But with Y Combinator’s demo day happening tomorrow, it seems likely that they’ll be receiving a lot of calls over the next few weeks, after which it may be reasonable to expect a seed round to come together.
If H3X’s prototypes perform as well in the wild as they do on the bench, they may very well enable a host of new electric transportation applications. We’ll be watching closely to see how the startup’s play affects the future of electric mobility.
]]>